realizată de Mhyca Munoz 4 ani în urmă
2062
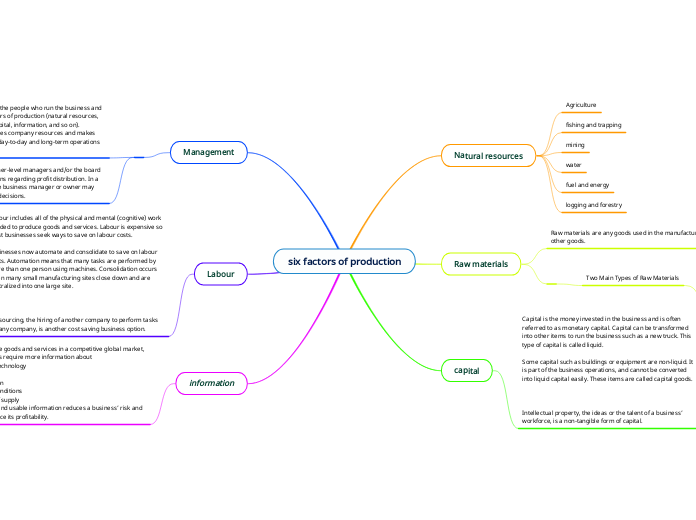
six factors of production
realizată de Mhyca Munoz 4 ani în urmă
2062

Mai multe ca acesta
Two Main Types of Raw Materials Ingredients ― raw materials that are combined or converted and become a part of the finished product. Supplies ― raw materials that do not become a part of the finished product, but are used in the product creation process.