ELECTROMAGNETIC
WAVES
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM
Radio Waves
e.g. λ: 10^3m
f: 10^4 Hz
Micro Waves
e.g. λ: 10^-2m
f: 10^8 Hz
Infrared
e.g. λ: 10^-5m
f: 10^12 Hz
Visible
e.g. λ: 10^-6m
f: 5 x 10^14 Hz
Ultraviolet
e.g. λ: 10^-8m
f: 3 x 10^16 Hz
X- Ray
e.g. λ: 10^-10m
f: 3 x 10^18 Hz
Gamma Ray
e.g. λ: 10^-12m
f: 3 x 10^20 Hz
Types of Electromagnetic Waves & Applications
Radio Waves
Characteristics
- Longest Wavelength
- Transverse Wave
Examples of Uses
- Used to transmit television
and radio programmes.
- Mobile Radio Communication
- Broadcasting
Microwaves
Characteristics
- Transverse Wave
Examples of Uses
- Microwave Ovens to
cook/heat up food.
- WiFi internet
-Speed Cameras
- Radars
Infrared
Characteristics
- Transverse Wave
- Given off by hot
objects
Examples of Uses
- Remote Controls
for TVs
- Short-Range
communications
-Security systems
(Burglar alarm
systems)
-Thermal Imaging
Visible Light
Characteristics
- Transverse Wave
- Only part of the
Electromagnetic spectrum
that is detectable by the
human eyes
Examples of Uses
-Lasers
-Laser Printers
-Light Bulbs
-DVD and CD Players
use lasers to read patterns
and translate it into sound
and video data.
Ultraviolet
Characteristics
- Transverse Wave
- Attracts insects
- Given off by the Sun
Examples of Uses
- Artificial Tanning
- Detecting forged bank notes
- Hardening dental filling
- Kill microbes and sterilize surgical equipment
- Used in Vitamin D deficiency treatment
X- Rays
Characteristics
- Transverse Wave
High Energy
Dangerous as it
can cause cell
damage and
cancers.
Examples of Uses
- X-Ray to see inside people
to diagnose injuries like bone
fractures.
- Airport Security checks to see
inside your luggages.
Gamma Rays
Characteristics
- Transverse Wave
-Extremely high
frequency waves
Pass through most
materials, difficult to
stop.
Examples of Uses
- Cancer treatment
(Radiotherapy)
- Tracers used by
doctors to see body
processes working
rather than seeing
still images
- Industrial tracers
- Sterilize food
(Irradiated food)
Dangers of Electromagnetic Waves
Radio Waves
- Generally not harmful
- However, large doses of
radio waves are believed to cause cancer,
leukemia and other disorders.
Micro Waves
- Prolonged exposure to significant
levels of microwaves is known to
cause "cataracts" in your eyes.
Infrared
- The danger to people from
too much Infra-Red is overheating.
Visible
- Too much light can damage
the retina in your eye. Although
the damage can heal, if it's too
bad it'll be permanent.
Ultraviolet
- Large doses of UV can damage
the retina.
- Large doses of UV can cause
sunburn and even skin cancer.
X- Ray
- X-Rays can cause cell
damage and cancers.
Gamma Ray
- Gamma Rays cause cell
damage and can cause a variety of
cancers.
- They cause mutations in
growing tissues, so unborn
babies are especially vulnerable.
Characteristics of EM waves
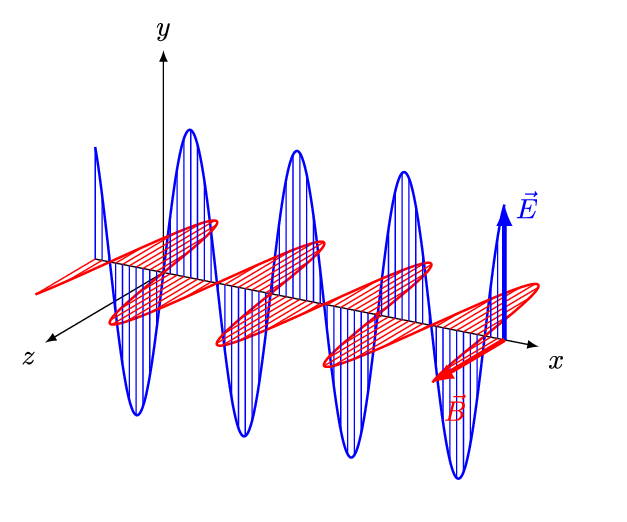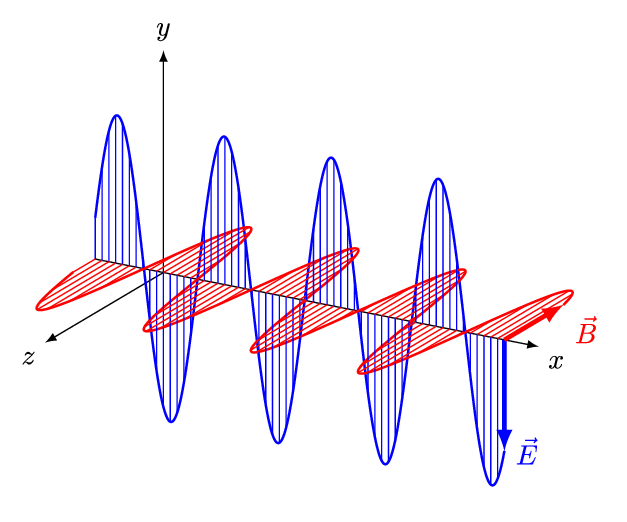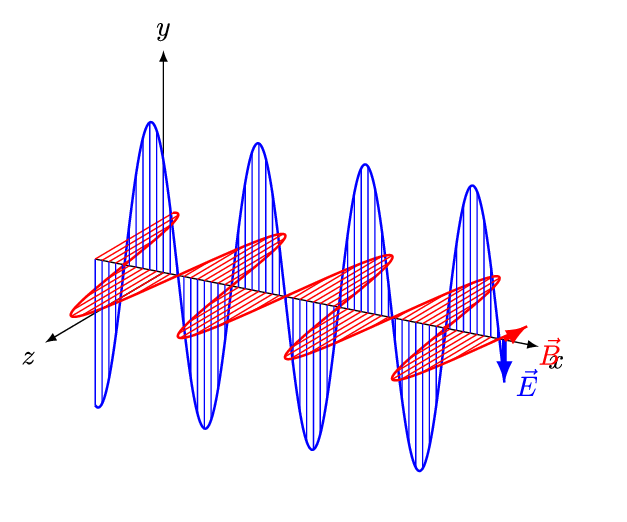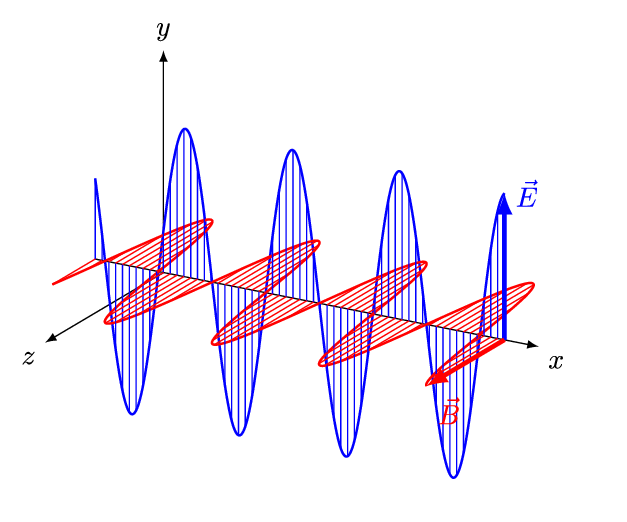
Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves. They comprise electric and magnetic fields that oscillate at 90 degrees to each other.
Able to travel through vacuum
And do not require a medium to travel from one point to another
Transfers energy from one place to another
For example; electromagnetic waves from the Sun transport thermal and light energy through space(i.e. vacuum) to Earth.
All travel at 3.0 x 10^8 m/s in vacuum
The wave speed equation : v = λ f
is applicable to all electromagnetic waves.
When travelling from one medium to another:
1)Speed Varies
2) Wavelength Varies
3) Frequency does not change
For example: when light travels from vacuum to water, its speed decreases from 3.0 x 10^8 m/s to 2.2 x 10^8 m/s. It's wavelength also decreases, while its frequency remains unchanged.
Obeys law of reflection and refraction
Carries no electrical charge
Longer Wave Length
Lower Frequency
Lower Energy
Shorter Wave Length
Higher Frequency
Higher Energy

Source(s)
-Oscillating circuits
TV
Radios
Source(s)
-Oscillating currents
in special vacuum tubes.
Microwave oven
Wifi
Source(s)
-Excitation of atoms
and molecules.
TV remote
Source(s)
-Excitation of atoms,
spark and arc flame.
Sun
Source(s)
-Excitation of atoms
and vacuum spark.
Sun
Source(s)
-Sudden retardation
of high energy electrons.
X-Ray machine
Source(s)
-Decay of radioactive
nuclei, fission and fusion
of atomic nuclei.