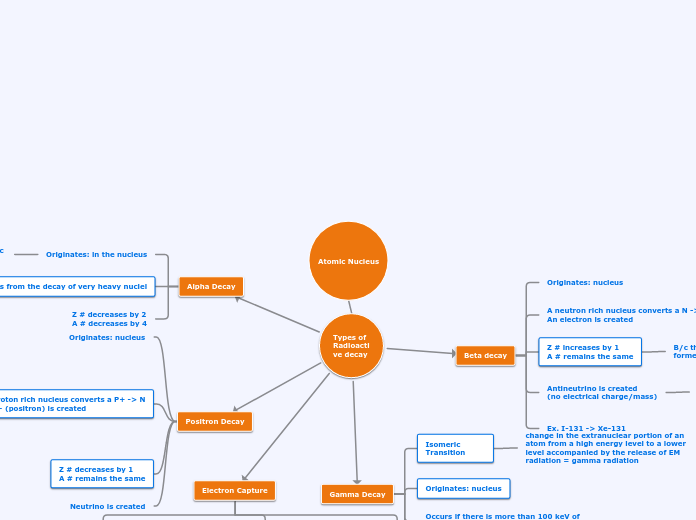
Atomic Nucleus
Types of Radioactive decay
Alpha Decay
Originates: in the nucleus
alpha particles are monoenergetic
range in matter is very short
Results from the decay of very heavy nuclei
Z # decreases by 2
A # decreases by 4
Beta decay
Originates: nucleus
A neutron rich nucleus converts a N -> P+
An electron is created
Z # increases by 1
A # remains the same
B/c the Z # changed, a new element is formed
Antineutrino is created
(no electrical charge/mass)
needed to conserve energy in the decay
it carries away the difference between B-
particle energy and the decay energy.
Ex. I-131 -> Xe-131
Gamma Decay
Isomeric Transition
change in the extranuclear portion of an atom from a high energy level to a lower level accompanied by the release of EM radiation = gamma radiation
Originates: nucleus
Occurs if there is more than 100 keV of excess energy,
Ex. Mo99-Tc-99m
Positron Decay
Originates: nucleus
A Proton rich nucleus converts a P+ -> N
A e+ (positron) is created
when the e+ is created it looses energy b/c its
colliding with surrounding matter, it gets attracted
to an electron and they spiral towards one another
before annihilation.
(mass of the e+ and e- is converted into pure EM
energy)
Z # decreases by 1
A # remains the same
Neutrino is created
Electron Capture
Originates: electron shell
Occurs when a orbital electron travels close to
the Proton rich nucleus
It is captured, and combined with a P+ to form a N
X-rays are emitted
Ex. Ga-67