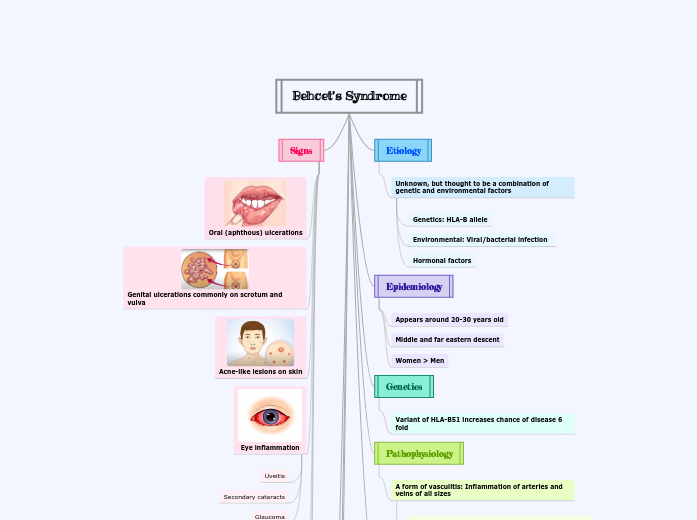
Behcet's Syndrome
Etiology
Unknown, but thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors
Genetics: HLA-B allele
Environmental: Viral/bacterial infection
Hormonal factors
Epidemiology
Appears around 20-30 years old
Middle and far eastern descent
Women > Men
Genetics
Variant of HLA-B51 increases chance of disease 6 fold
Pathophysiology
A form of vasculitis: Inflammation of arteries and veins of all sizes
Immune dysregulation: Abnormal response to certain antigens which leads to an increased production of inflammatory cytokines.
Diagnostic Criteria:
Recurrent oral ulcerations
Painful aphthous ulcerations with at least 3 episodes in any 12-month period
PLUS any two of the following:
Recurrent, painful genital ulcerations
Aphthous ulceration or scarring
Eye lesions
Anterior or posterior uveitis, cells in vitreous on slit-lamp examination or retinal vasculitis
Skin lesions
Erythema nodosum-like lesions; papulopustular skin lesions or pseudofolliculitis with characteristic acneiform nodules
Pathergy test
Papule 2 mm or more in size, developing 24-48 hours after pricking the skin with a 20-25 gauge needle
Signs
Oral (aphthous) ulcerations
Genital ulcerations commonly on scrotum and vulva
Acne-like lesions on skin
Eye inflammation
Uveitis
Secondary cataracts
Glaucoma
Arthritis
Asymmetric and nondestructive
Aneurysms and blocked/narrowed vessels
Erythema nodosum-like lesions
Symptoms
Painful sores/ulcers in the mouth, tongue, and back of throat
Blurry vision, eye redness, pain, sensitivity to light, and possible vision loss
Painful sores or raised, tender nodules on skin, especially on lower legs
Painful, red, and open genital lesions
Joint swelling and pain
Headache, fever, poor balance, disorientation, stroke
Abdominal pain, bleeding, and diarrhea
Treatment
Treat by organ system involved
Pharmaceutical treatment
Glucocorticoids
DMARDs-azathioprine/methotraxate
Otezla
TNFa inhibitor
Health Promotions
No specific disease prevention screening guidelines because of the rarity of the disease, but after diagnosis, the patients should have regular follow ups and screenings for complications:
Opthalmologic exams: prevent vision problems
Dental check-ups: monitor and manage oral ulcers
Psychological support: screen for anxiety and depression because of chronic nature of the disease
Blood tests to monitor inflammatory markers
Imaging to assess for vascular complications or involvement of other organs
Regular monitoring of cardiovascular health due to increased risk of thromboembolic events
Health Lifestyle Education
Healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods
Regular physical activity
Avoid smoking and excess alcohol consumption
Stay up to date on vaccines