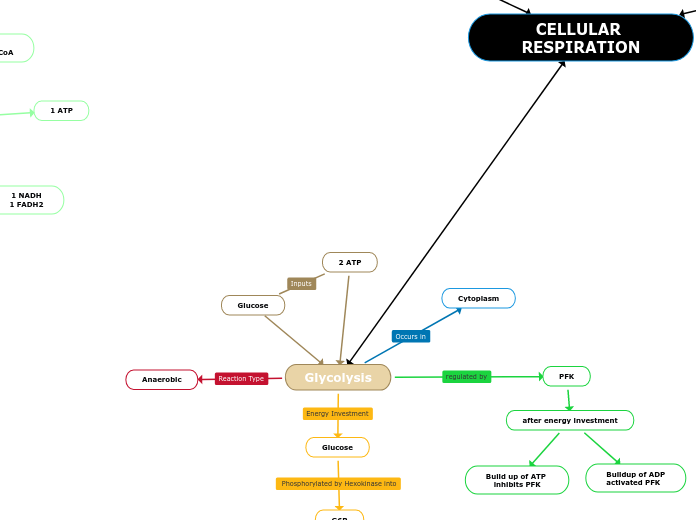
2 ATP
Glycolysis
Anaerobic
Glucose
G6P
F6P
Cytoplasm
PFK
after energy investment
Build up of ATP
inhibits PFK
Buildup of ADP
activated PFK
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Factors affecting rate of respiration
higher temp= faster reaction rates
Higher Concentration = faster reaction rate
Will reach a point of saturation
where it will be at peak production
Cycle is dependent on oxygen
needs it to drive the ETC (EN)
Alternatives to Glucose
Catabolism
Lipid Catabolism
triglycerides into glycerol
and fatty acids
2 glycerol molecules
can combine to form 2 things:
2 DHAP which then
turn into G3P
Glucose
enter mitochondrial matrix
undergo B-oxidation to become
acetyl-CoA
2 C acetyl group removed
binds with CoA to make Acetyl-CoA
12-C fatty acid could produce
6 Acetyl-CoA molecules
1 ATP
1 NADH
1 FADH2
Protein Catabolism
Occurs in Liver
amino acids
through hydrolysis
can enter through
different stages
Other Carbohydrates
Glucose
F16BP
G3P
BPG
3PG
2PG
PEP
Pyruvate
DHAP
G3P
BPG
3PG
2PG
PEP
Pyruvate
4 ATP
2 NADH
2 Water
2 ATP
2 Pyruvate
Fermentation
Alcohol
Pyruvate converted
into ethanol and CO2
Occurs in
Yeast
Microorganisms
Alcohol Dehydrogenase
Mainly in Plants
Anaerobic
Lactate
Pyruvate
Decarboxylase
Pyruvate converted
into lactic acid and energy
Lactate Dehydrogenase
Mainly in Animals
Muscle Cells
Pyruvate Oxidation
Aerobic
Cytoplasm into Matrix
Pyruvate enters
Mitochondria
via transport protein
Energy Harvesting
Pyruvate is decarboxylated
and CO2 is released
it now has 2 Carbons
Coenzyme A is attached
to make Acetyl CoA
Krebs Cycle
Aerobic
Mitochondria
Matrix
2 Cycle per Glucose
Products
4 CO2
2 ATP
6 NADH
Oxidative Phosphorylation
2 Steps
Electron Transport
Chain
Aerobic
Inner Mitochondrial
Membrane
Delivery of Electrons
by NADH and FADH2
NAD+ & FAD
Electron Transfer
& Proton Pumping
Electrochemical
Gradient
Splitting of Oxygen
to form Water
Movement of
Electrons
NADH
Goes through
Complex's 1, 3, 4
10 Protons
2.5 ATP
FAD2
Goes through
Complex's 2, 3, 4
6 Protons
1.5 ATP
Complex I
Complex II
Coenzyme Q
Complex III
Cytochrome C
Complex IV
Oxygen
Electronegative, Drives ETC.
Removes 2 electrons from
Complex IV and 2 Protons from
the matrix (this makes water)
Intermembrane
Space
Chemiosmosis
Inner Mitochondrial
Membrane
Aerobic
Pumps protons from inner
membrane back down the (H+)
gradient which results in the
making of ATP through ATP
synthase.
ATP SYNTHASE
As protons move down
the gradient ADP is turned
into ATP.
Production of ATP
is called Oxidative
Phosphorylation
Transport
Protein
Final Step of
Cellular Respiration
NADH
Accepts 2
electrons
Accepts 2
protons
FADH2
Accepts 2
electrons
Accepts 2
protons
2 FADH2
NAD+ is reduced
into NADH
Acetyl CoA
Oxaloacetate
Citrate
CoA and H2O
Isocitrate
a - Ketoglutarate
CO2
NAD+ into
NADH
Succinyl-CoA
CO2
Coenzyme A is added
NAD+ into
NADH
Succinate
CoA
Fumarate
FAD into FADH2
Malate
H2O
ATP
PFK
Buildup of Citrate
inhibits PFK (stops it)
NAD+ into
NADH
STARTS AND
ENDS HERE