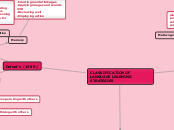
CLASSIFICATION OF LANGUAGE LEARNING STRATEGIES
Oxford's (1990)
INDIRECT STRATEGIES
Metacognitive Strategies
A. Centering your learning
Arranging and planning your learning
Evaluating your learning
Affective Strategies
Encouraging yourself
Lowering your anxiety
Taking your emotional temperature
Social Strategies
Asking questions
Emphathising with others
Cooperating with others
DIRECT STRATEGIES
Memory
-Creating mental linkages
-Applying images and sounds
330
-Reviewing well
-Employing action
Cognitive
-Practising
-Receiving and sending
messages strategies
-Analysing and reasoning
-Creating structure for
input and output
Compensation strategies
-Guessing intelligently
-Overcoming limitations
in speaking and writing
O'Malley's (1985)
Meta-cognitive
Strategies
-to express
executive function
-strategies which require
planning for learning
-thinking about the
learning process as it is
taking place
-monitoring of one's
production or comprehension
-evaluating learning after an
activity is completed.
Cognitive
Strategies
specific learning tasks
that involve more direct
manipulation of the
learning material itself
Socioaffective
Strategies
related with
social-
mediating
activity and
transacting
with others.
Rubin's (1987)
Social Strategies
activities that afford
learners the opportunities to
be exposed to and practise
their knowledge
Learning Strategies
Cognitive Learning Strategies
Clarification / Verification
Guessing / Inductive Inferencing
Deductive Reasoning
Practice
Memorization
Monitoring
Metacognitive Learning Strategies
planning
prioritising
setting goals
self-management
Communication Strategies
focus on the process of participating in a conversation and getting meaning
across
clarifying what the speaker intended