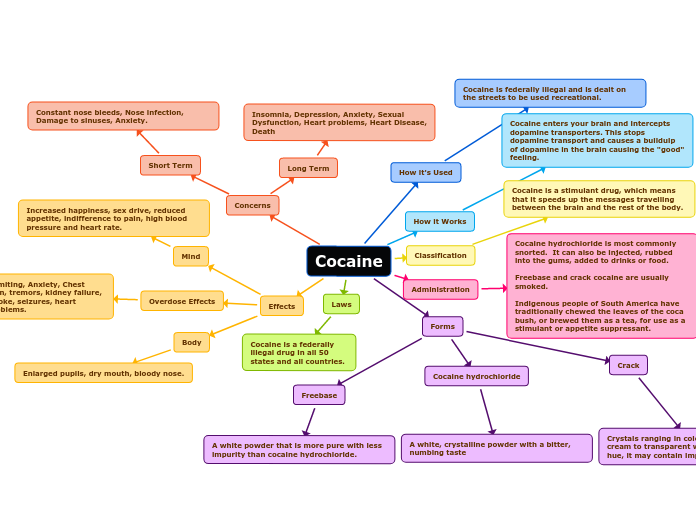
Cocaine
Forms
Cocaine hydrochloride
A white, crystalline powder with a bitter, numbing taste
Freebase
A white powder that is more pure with less impurity than cocaine hydrochloride.
Crack
Crystals ranging in colour from white or cream to transparent with a pink or yellow hue, it may contain impurities
Administration
Cocaine hydrochloride is most commonly snorted. It can also be injected, rubbed into the gums, added to drinks or food.
Freebase and crack cocaine are usually smoked.
Indigenous people of South America have traditionally chewed the leaves of the coca bush, or brewed them as a tea, for use as a stimulant or appetite suppressant.
Classification
Cocaine is a stimulant drug, which means that it speeds up the messages travelling between the brain and the rest of the body.
Laws
Cocaine is a federally illegal drug in all 50 states and all countries.
How it Works
Cocaine enters your brain and intercepts dopamine transporters. This stops dopamine transport and causes a builduip of dopamine in the brain causing the "good" feeling.
Effects
Body
Enlarged pupils, dry mouth, bloody nose.
Mind
Increased happiness, sex drive, reduced appetite, indifference to pain, high blood pressure and heart rate.
Overdose Effects
Vomiting, Anxiety, Chest pain, tremors, kidney failure, stroke, seizures, heart problems.
Concerns
Short Term
Constant nose bleeds, Nose infection, Damage to sinuses, Anxiety.
Long Term
Insomnia, Depression, Anxiety, Sexual Dysfunction, Heart problems, Heart Disease, Death
How it's Used
Cocaine is federally illegal and is dealt on the streets to be used recreational.