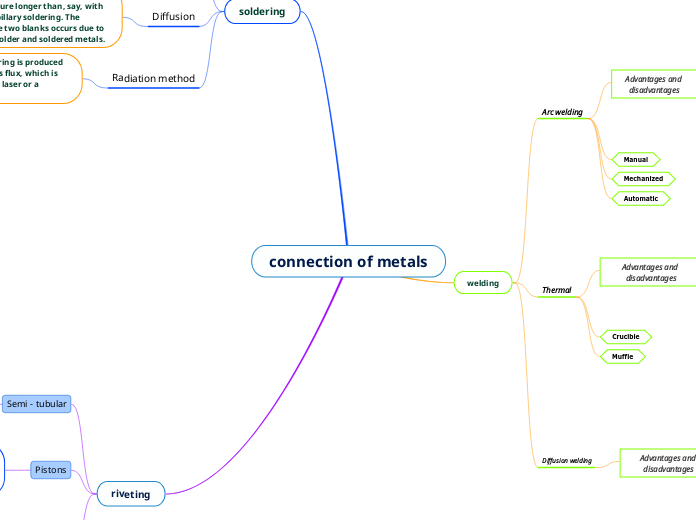
connection of metals
welding
Arc welding
Advantages and disadvantages
+ does not require complex training;
+ high process performance;
+ low cost of consumables (welding electrodes);
+ the simplicity of the process makes it easy to automate and mechanize it;
+ a small area of surface heating.
- binding to the power grid;
- inability to work without current converters (rectifiers, inverters) and transformers;
- the presence of a preliminary stage of preparation of the welded surfaces.
Manual
Mechanized
Automatic
Thermal
Advantages and disadvantages
+ excellent joint strength indicators.
+ low labor intensity of work.
+ low cost.
+ minimum metal consumption.
- irregularities on the surface of the workpiece and the presence of an oxide film significantly impairs the quality of the joint.
- thermal welding is possible only with metals that are close in terms of refractoriness
Crucible
Muffle
Diffusion welding
Advantages and disadvantages
+ to combine homogeneous and heterogeneous solids;
+ avoid deformation of parts;
+ do not use consumables in the form of solders and fluxes;
+ get waste-free production;
+ receive any area of the contact connection zone, limited only by the possibility of equipment;
+ ensure reliable electrical contact
- the need to use specific expensive equipment;
- the requirement to have special knowledge, skills and understanding of the work process;
- time spent on thorough pre-processing of workpieces;
- the difficulty of checking the quality of the seam without the need for its destruction.
soldering
Capillary
The solder is melted, it heats up and fills the space between the two prepared parts. The wetting of the surface of the parts and the retention of the solder is largely due to the effect of capillarity.
Diffusion
The solder inside the seam zone is kept at a certain temperature longer than, say, with conventional capillary soldering. The connection of the two blanks occurs due to the diffusion of solder and soldered metals.
Radiation method
The radiation type of soldering is produced due to a powerful luminous flux, which is formed by a quartz lamp, a laser or a cathode defocused beam.
riveting
Semi - tubular
They require less effort during installation, but they also have low strength. They are used in connections with a small mechanical load.
Pistons
They are used for low-load connections, they are made mainly of soft metals (aluminum and alloys, copper).
Threaded
For connecting parts with thin walls (up to 0.3 mm). They differ in that the inner part has a threaded thread, the outer one has a vertical notch that prevents rotation around its axis. A screw is twisted inside, pulling the free part of the housing to the junction. This is how it turns out — due to crumpling — the closing head.