English Grammar
Present perfect
Structure
Positive
Subject + have/has + v3 + object
Negative
Subject + have/has + not + v3 + object
Interrogative
Have/has + subject + v3 + object +?
Example
Positive
I have bought a ticket for every game this season
Negative
She has not watched 'Titanic' yet.
Interrogative
Have you had fun today?
Present continous
Structure
Positive
Subject + to be + base + ing
Negative
Subject + to be + not + base + ing
Interrogative
Am/is/are subject + verb (ing) + pbject + ?
Use
An ongoinf action,
Events
Something that has happened around us
Example
Positive
She is talking.
Negative
She is not (isn't) talking
Interrogative
Are you dancing?
Present simple
Structure
Positive
3rd person singular (he, she, it) infinitive + -s
do/does + not + infinitive of the verb
Do/does + he/she/it/I/we/you/they + verb + ?
Use
Regular actions
Actions that are happening now
Schedules
Habits
Facts
Instructions
Example
Positive
She plays with a ball.
Negative
She does not play with a ball.
Interrogative
Does Jack play football?
Modals
Use
Are used together with main verbs to represent the ability, possibility and probability of a subject to perform an action and to emphasize the necessity of an action.
Something that is
Necessary
Advisable
Permissible
Possible
Probable
Expressing necessity
Be able
Can
Could
Be going to
Will
Shall
Be supposed to
Had better
Have to
Must
Gave got to
Must
Expressing necessity 0.2
Present
Must
Have
Have got
Past
Had to
Lack of necessity
Not have to
Prohibition
Must
Musn't
Advisability
Present
Should
Shouldn't
Oght to
Past
Had better
Had better not
Should have + V past + participle
Example
Shall I make some tea for you
Relative pronouns
Use
To connect an independent clause to a relative clause
To provide more information about the subject it relates to
Who, whom, whose, that and which
Example
Sheela, who is a teacher, also works as a social worker
Relative clauses
Use
Modifies a noun
Provides more information about it
Types
Defining clauses
Essential information
We do NOT use commas around them
If there’s a subject after the pronoun, we can eliminate the pronoun
Not-defining clauses
Extra information
We use commas around them
We always use a relative pronoun
Never use THAT
Examples
The reason why Jane was crying is unknown.
Relative adverbs
Use
They provide more information
Time
Place
Reason
Connect the relative clause to the main clause.
Example
When
Refers to a time
The day when we met was unforgettable.
Why
I understand the reason why she was upset.
Where
Refers to a place, information about location
The house where I grew up is now a museum.
Imperatives
Structure
Base Form of Verb] (+ Optional Subject) (+ Optional Modifier)
Example
Close the door
Future forms
Tenses
Perfect
For action that will happen/be completed by a certain time in the future
Simple
For things we thing or believe will happen in the future
Continous
To talk about situations or actions that will be in progress at a certain time in the future
perfect continous
To talk the duration of a situation until a certain time un the future
Example
Perfect
She'll write the e-mail after lunch
Simple
He will be 50 next month.
Continous
We’ll be coming next weekend.
Perfect sontinous
By the end of the year, she will have been working on the publication for over ten years.
Future B2 forms
Structure
Positive
Subject + Will + Base form of the verb.
Negative
Subject + Will not/Won’t + Base form of the verb.
Interrogative
Will + Subject + Base form of the verb.
Won’t + Subject + Base form of the verb
Use
To talk about something that will happend
Example
I will play tennis.
Articles
Use
A
Before nouns that begin with a consonant sound.
An
Before nouns that begin with a vowel sound.
The
To specify a particular noun.
Example
A
A car
An
An apple
The
The book on the table
Passive
Present
Structure
Positive
Subject + am /ist/are + verb in past participle
Negative
Subject + am not/isn't/aren't + verb in past participle
Interrogative
Am/is/are + subject + past participle verb
Use
When we want to emphasize the action (the verb) and the object of a sentence rather than the subject.
Example
Positive
The car isn't washed every week.
Negative
A lot of cod is caught in the North Atlantic.
Interrogative
Is this painting drawn by you?
Past
Structure
Positive
Subject + was/were + past participle verb
Negative
Subject + wasn't/were n't+ past participle verb
Interrogative
Was/Were + subject + past participle verb
Use
Depends on the subject of the sentence. For singular subjects (he, she, it), "was" is used. For plural subjects (we, you, they), "were" is used
Gerund
Structure
S + verb + to + verb ing + cmp + .
Example
She's learning to play the piano in her school.
Past simple
Use
To talk about actions that were completed in the past before the present.
Structure
Positive
Subject + verb + ed
Did + subject+ infinitive
Negative
Subject + did not + infinitive
Did not + subject + infinitive
Example
My father died last year.
Past continous
Structure
Positive
S + was/were + verb (ing) + object
S + was/were + not + verb (ing) + object
interrogative
Was/were + S + verb (ing) + object?
Use
Past habits
Past action / interrupted
Background for a story
Ongoing actions
Example
They were eating at the restaurant.
Past perfect
Use
Action before another action started
Also use “before”
Action
Was not done
Structure
Positive
S + had + verb (past participle) +complement
Negative
S + had + not + verb (past participle) +complement
Interrogative
Had + S + verb (past participle) + complement?
Example
Positive
The film had started before we arrived.
Negative
They hadn't finished their homework
Interrogative
Had he studied for the test?
Past perfect continous
Use
To talk about the cause of something in the past.
Structure
Positive
S + had + been + v-ing + .
S+ had not/hadn´t + been + v-ing + .
Interrogative
Had + S + been + v-ing + ?
Example
Helen had been listening the same music for 4 hours
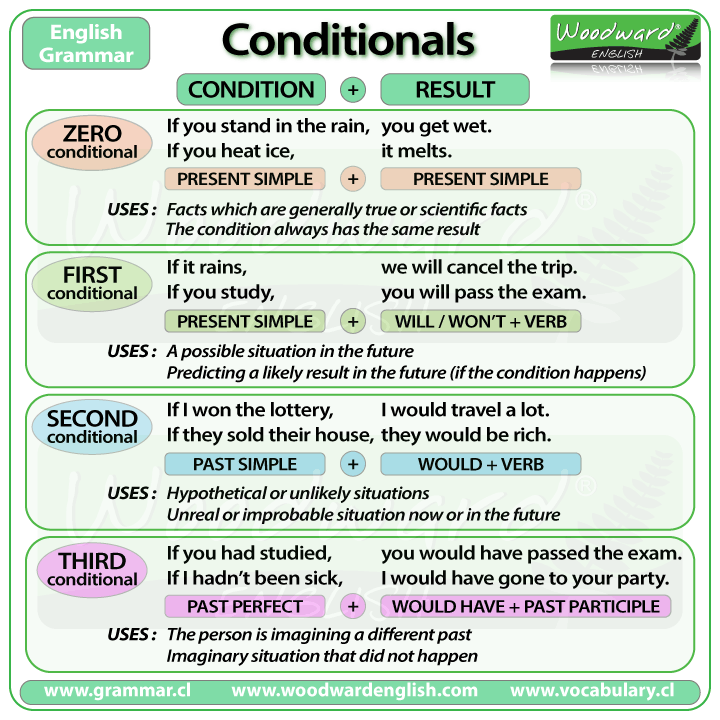
Conditional if
Use
to describe a possible situation
Subtopic
Conditional wish
Use
To regret something

Subtopic
Would
Use
Repeated past actions that don't happen any more.
Structure
Positive
S + would + main verb base + .
Negative
S+ would not/ wouldn’t + main verb base + .
Interrogative
Would + S + main verb base + ?
Example
When I was young I would play tennis.
Used to
Use
No longer true actions
Repeated actions
State a situation
Structure
Positive
S + used to + inf. verb .
Negative
S + didn’t/did not + use to + m. verb
Interrogative
Did/Didn’t + use to + m. verb
Example
We used to go to the seaside every summer when I was a kid.
Infinitive
Use
verb - other verb
different verbs
both - meaning (different)
Structure
S + verb + verb -ing + cmp + .
Example
both - meaning (different)
Determiners
Use
Modifies, describes, or introduces a noun.
Types
Definite and indefinite articles
Demonstrative determiners
Possessive determiners
Determiners of difference
Numbers
Distributive determiners
Interrogative determiners
Subtopic
Quantifiers
Example
Definite and indefinite articles
The moon looks beautiful tonight.
Demonstrative determiners
I don’t want to sit at this table. I want that table near the window.
Possessive determiners
Penelope brought her cat to the vet.
Determiners of difference
Other shoes might match your outfit better.
Numbers
Cardinal numbers|I’m close with my four siblings.
Distributive determiner
Each employee was given a raise
Interrogative determiners
What height is the Empire State Building?
Quantifiers
There are already several people waiting for a table at this restaurant.
Pronouns
Use
Replace nouns to make sentences less repetitive and more concise.
To avoid redundancy, and improve communication.
Types
Personal
He
She
They
Possesive
His
Her
Their
Demostrative
This
That
Those
Reflexive
Myself
Herself
Themselves
Interrogative
Who
What
Which
Indefinited
Everyone
Nobody
All
Nouns
Use
To identify something
Types
Common
Prpper
Singular
PLural
Contable
Uncountable
Concrete
Abstract
Collective