Tectosilicate
Phyllosilicates
Inosilicates
Inosilicates
orthosilicates
Tetrahedral structure
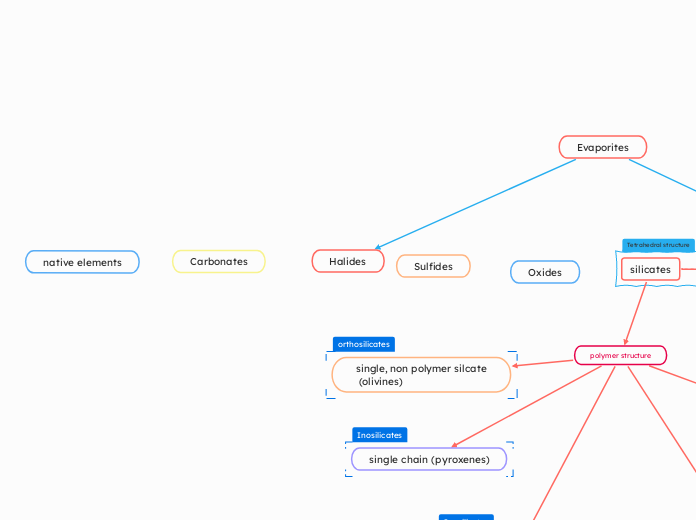
Halides
Clay
Quartz
Isomorphous sub Si+4 -> Al3+
-4 charge from oxygen pr. cation
Carbonates
Phosphates
silicates
Sulfates
native elements
Sulfides
Difference in Al+3 and Fe+ ion size
Low negative permanent charge
Low-level
Feldspar
need for extra cations to negate the charge
Octahedral
polymer structure
single, non polymer silcate
(olivines)
Double chain (amphiboles
single chain (pyroxenes)
Oxides
Tetrahedral
K-feldspar
Na-feldspar
K+ in the interlayer gap
Hydrogen vs vanderwalls
Clay
1:1 layer
Kaolinite
OH-groups(octahedral) and O^-2 group (tetrahedral)
2:1 layer
vermiculite
Smectite
Illite
2:1:1 Layer
Chlorite
Evaporites
Layer silicates (Micas)
Framework silicates (3D)
Octahedral
Strength of intermolecular bonding
Swelling from hydration
Isomorphous sub
Divalent vs trivalent cation
Negative permanent charge
Effective charge
surface area: Fixed vs interlaygap
Presence of water and cations in interlayer gap
Expansion when heated
octhedral in
interlayergap
resistent to hydration
CEC
Ph-dependent charge
OH-groups
releasing vs apsorption of H+
pH-levels
Oxides
aluminium-oxides
Gibbsite
Iron-Oxides
Goethite