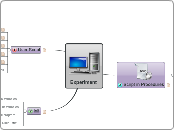
Experiment

Script in Procedures
Block specific
Get values of list attributes
Set up Canvasses
Draw Canvasses
Keep track of participant scores
Give feedback to respnses (visual/auditory)
Trial specific
Get values of list attributes
Set up Canvasses
Draw Canvasses
Keep track of participant scores
Give feedback to respnses (visual/auditory)
randomize
User Script
Constants
Type declarations
Global Variables (incl. arrays etc.)
Functions
Set up Canvasses
Subroutines
Set up Canvasses
Init
Initialize global variables
Set up variables
Logic that remains the same for the rest of the program
Set canvasses that are dim-med in User Script