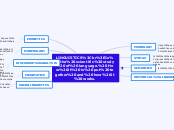
LINGUISTICS
Is the scientific study of language. How it is put together and how it works.
PHONOLOGY
Uses phonetics in order to see how sounds or signs are arranged in a system for each language.
SYNTAX
Is the study of how phrases, clauses and sentences are constructed and combined in particular languages.
SEMANTICS
Is the study of meanings.
HISTORICAL LINGUISTICS
Is the study of how languages have changed over time.
PHONETICS
Study of the sounds of speech and how they are made and produced in the body.
MORPHOLOGY
Looks at how individual words are formed from smaller chunks of meaningful units called morphemes.
DISCOURSE ANALYSIS
looks at bigger chunks of language - texts, conversations, stories, speeches, etc. Different types of these use language differently, and there can even be differences in how a language is used based on the genre.
PRAGMATICS
It involves the study of how speakers of a language use the language to communicate and accomplish what they want.
SOCIOLINGUISTICS
It is the study of society and language and how it affects each other