Macro-molecules
Proteins
Examples
Skin
Muscle
Hormones
Fingernails, Claws
Enzymes
Hair
Functions
Hormones
Movement
Immune System
Enzymes
Elements
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Carbon
Nitrogen
Unique Characteristics
Amino Acids are linked by peptide
bonds. Each amino acid is the same
except for the variable (function) group
Monomer
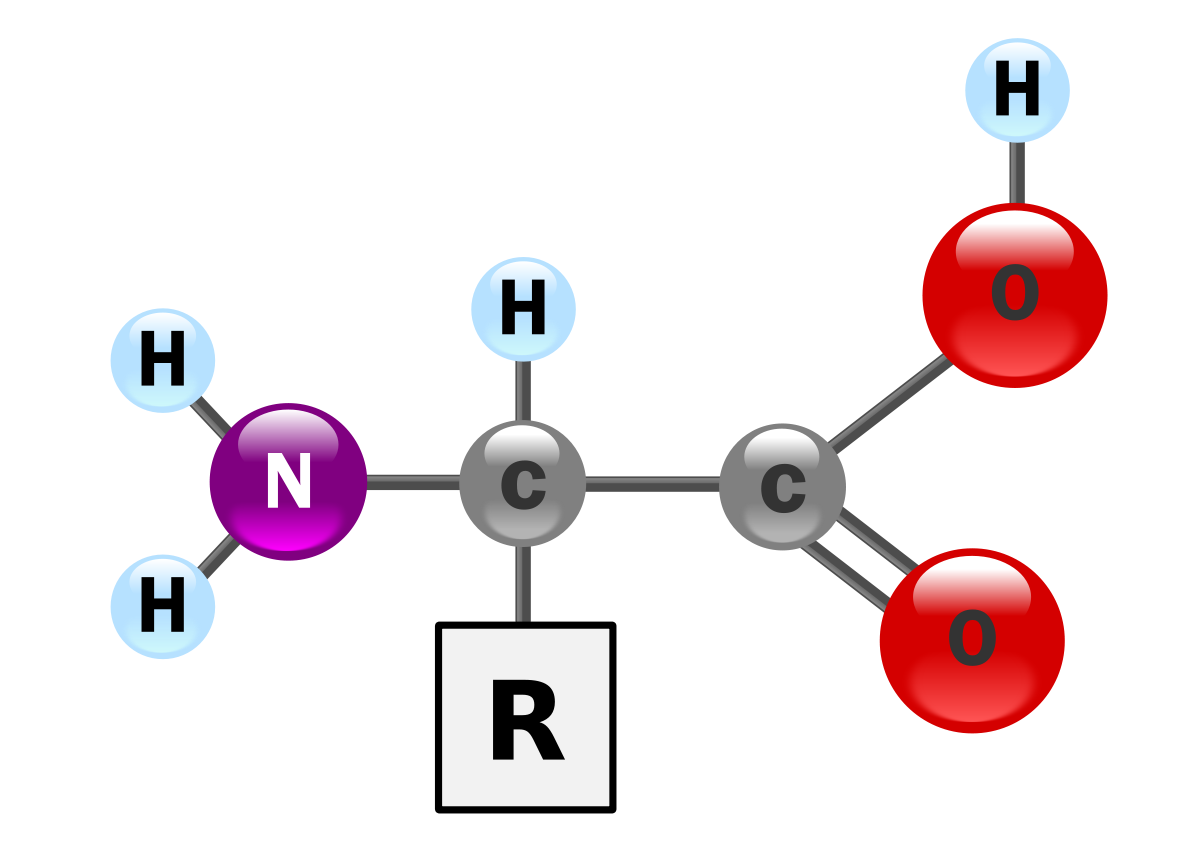
Amino Acid
Lipids
Examples
Fats
Oils
Waxes
Steroids
Phospholipids
Monomer

Triglycerides
Functions
Insulates Body
Cushions Organs
Energy Storage
Unique Characteristics
Lipids are Non-Polar and
Hydrophobic (Doesn't like
water.)
Elements
Hydrogen
Carbon
Oxygen
Nucleic Acids
Elements
Nitrogen
Phosphorous
Oxygen
Hydrogen
Unique Characteristics
RNA is a single nucleotide chain,
while DNA is a double nucleotide
chain spiraled in a double helix.
Examples
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Monomer
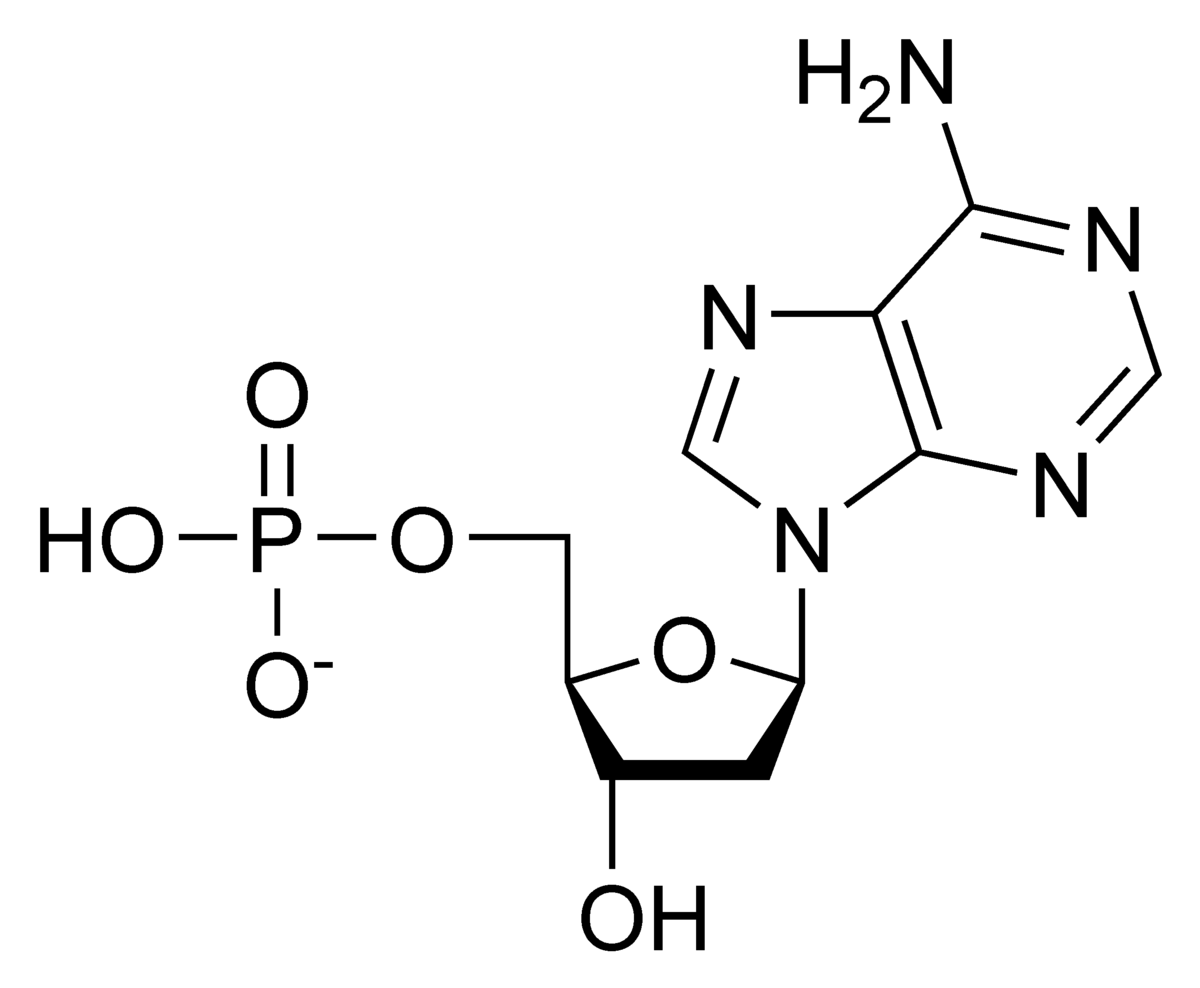
Nuleotide
Functions
Store Hereditary Information
Transmit Hereditary Information
Series of bases encodes information
Stored information is passed
from parent to offspring
Carbohydrates
Monomer

Monosaccharides
Elements
Hydrogen
Carbon
Oxygen
Functions
Quick Energy
Energy Storage
Structure
Examples
Glycogen
Cellulose (Cell Wall)
Starches
Sugar
Unique Characteristics
Cellulose is the reason for carnivores
and herbivores. Cellulose is found in all
plants (All plants have cell walls) but
not all animals can digest cellulose
leading to some animals being herbivores
(Those that can digest cellulose)
and some animals being carnivores(Those
that can not digest cellulose.)