Math
Functions
Trig Functions
Sine Waves
f(x)=asin(k(x-h))+c
(x,y)---}((x/k)+h,ay+c)
Cosine Waves
f(x)=acos(k(x-h))+c
(x,y)---}((x/k)+h,ay+c)
4 Primary Functions
Quadradic
f(x)=x^2
Rational
f(x)=√x
Absolute
f(x)=|x|
Reciprocal
f(x)=1/x
Exponential Function
Decay Model
f(x)=ar^x (where r is a decimal / fraction)
Growth Model
f(x)=ar^x
f(x)=A₀(1+i)^x
Function Definitions
Discrete:
A function that has specific data set.
Aka: several points in data.
Ex: # of students in a class, only a set #
as you cannot have 1/2 of a student.
Recursive:
A function that calls upon previous
numbers within the function.
Ex: the Fibonacci sequence that
uses the previous numbers in the sequence
to make the new number.
tn=t(n-1)....
Continuous:
A function where numbers can be
any value within a set.
Ex: time it took to complete some task
at any point you could say 1/2 of a second,
1 microsecond,
1 minute but there is a defined set if the task for example took 10 minutes.
General Trig
Identities
tanx=sinx/cosx
secx=1/cosx
cscx=1/sinx
cotx=1/tanx
1=(cosx)^2+(sinx)^2
Trig Problems
3D Problems
Ambiguous Case
h=asinB
2D Problems
Special Angles
Angles for: 30° and 60°
Angles for 45°
Unit circle
This is the CAST rule
Series / Sequences
Series
A series is a set of numbers that
have an end to them.
Ex: the keys on a keyboard
Sequence
A sequence is a set of numbers
that have no set end to them.
Ex: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, ... this would go on
forever
Arithmetic
Arithmetic Series / Sum Formula
Sn=n(a+tn)/2
Sn=n(2a+d(n-1))/2
Arithmetic Sequence
a+d(n-1)
Geometric
Geometric Sequence
ar^n-1
Geometric Series / Sum Formula
Sn=a(r^n-1)/r-1
Financial Applications
Annuities
Present Value

PV=R(1-(1+i)^-n)/i
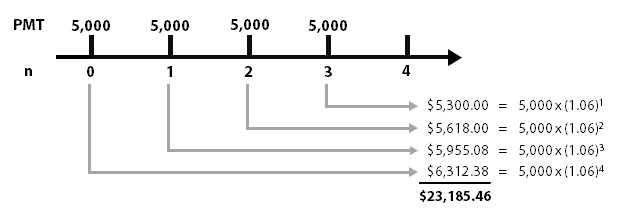
Future Value
Annuities are compounding
interests where you are
adding more money into
the account as time goes
on, alongside with the
interest earned on the money
from before.
Compounding Interest
A=P(1+i)^n
The interest is the rate, r,
by the compounding period.
The time, n, is
the amount of time multiplied
by the compounding period.
Simple Interest
I=Prt
A=P+I