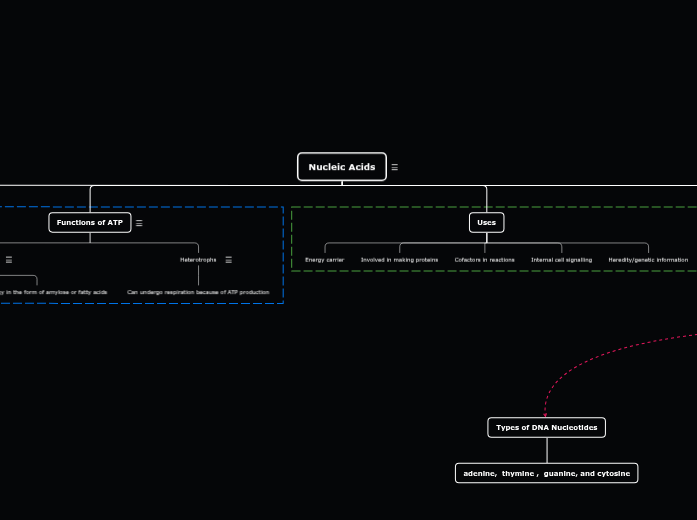
Nucleic Acids
Plays a Role in Food Systems
Limitations to the Food System
Natural Resources are Under Pressure
Too Rich in fat, sugar, salt, and meat
Malnutrition
Waste
Functions of ATP
Autotrophs
grows new tissue
stores energy in the form of amylose or fatty acids
Heterotrophs
Can undergo respiration because of ATP production
Uses
Energy carrier
Involved in making proteins
Cofactors in reactions
Internal cell signalling
Heredity/genetic information
Structure
Nucleotide
One or more phosphate functional groups
5-carbon sugar
DNA
Single strand
Double strand
RNA
Single strand
Double strand
Nitrogenous base
Purines
Pyrimidines