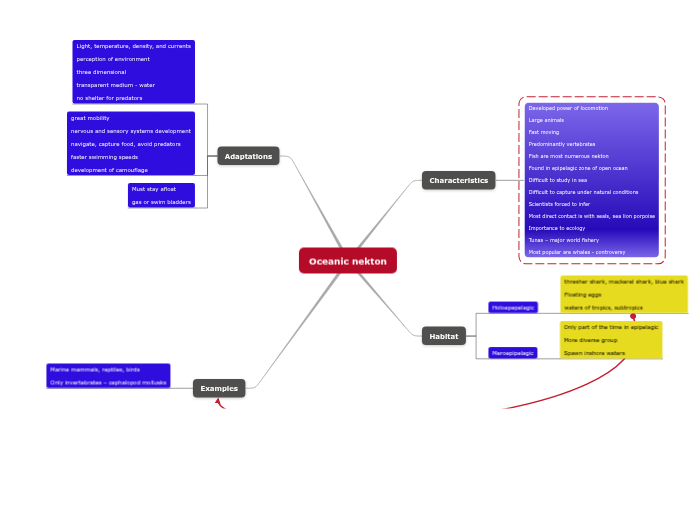
Oceanic nekton
Characteristics
Developed power of locomotion
Large animals
Fast moving
Predominantly vertebrates
Fish are most numerous nekton
Found in epipelagic zone of open ocean
Difficult to study in sea
Difficult to capture under natural conditions
Scientists forced to infer
Most direct contact is with seals, sea lion porpoise
Importance to ecology
Tunas – major world fishery
Most popular are whales - controversy
Habitat
Holoepepelagic
thresher shark, mackerel shark, blue shark
Floating eggs
waters of tropics, subtropics
Meroepipelagic
Only part of the time in epipelagic
More diverse group
Spawn inshore waters
Adaptations
Light, temperature, density, and currents
perception of environment
three dimensional
transparent medium - water
no shelter for predators
great mobility
nervous and sensory systems development
navigate, capture food, avoid predators
faster swimming speeds
development of camouflage
Must stay afloat
gas or swim bladders
Examples
Marine mammals, reptiles, birds
Only invertebrates – cephalopod mollusks