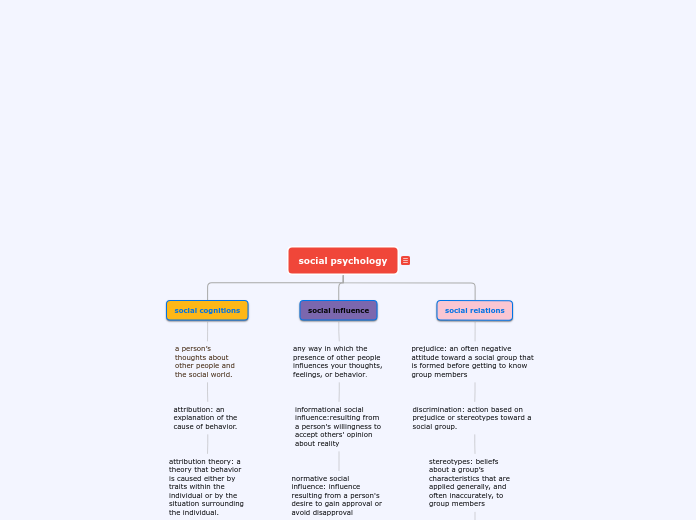
social psychology
social cognitions
a person’s thoughts about other people and the social world.
attribution: an explanation of the cause of behavior.undefined
attribution theory: a theory that behavior is caused either by traits within the individual or by the situation surrounding the individual.undefined
ATTITUDE PERSUASION STRATEGY
DESCRIPTION
Central route persuasion
Directly explain the actual benefits.
Peripheral route persuasion
Use “smoke and mirrors” to make it seem great.
Foot-in-the-door technique
Get them to agree to something little before asking for something big.
Door-in-the-face technique
Ask for something way too big first, then what I actually want will seem reasonable.
Lowball technique
Get them to agree, then jack up the price.
social influence
any way in which the presence of other people influences your thoughts, feelings, or behavior.
informational social influence:resulting from a person's willingness to accept others' opinion about realityundefined
normative social influence: influence resulting from a person's desire to gain approval or avoid disapproval
conformity: changes in an individual’s behavior to correspond to the behavior of a group of other people.
obedience: changes in an individual’s behavior to comply with the demands of an authority figure.
social relations
prejudice: an often negative attitude toward a social group that is formed before getting to know group members
discrimination: action based on prejudice or stereotypes toward a social group.
stereotypes: beliefs about a group’s characteristics that are applied generally, and often inaccurately, to group membersundefined
Aggression is behavior intended to cause harm or death