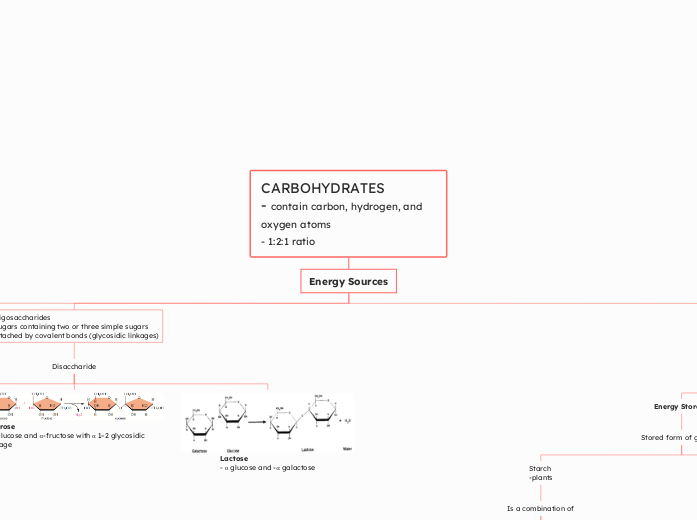
CARBOHYDRATES
- contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
- 1:2:1 ratio
Energy Sources
Monosaccharide
-simple sugars
-building blocks of carb
Isomers are
Glucose C₆H₁₂O₆
Types
α -glucose
β-glucose
Glactose C₆H₁₂O₆
Fructose C₆H₁₂O₆
Oligosaccharides
- sugars containing two or three simple sugars
-attached by covalent bonds (glycosidic linkages)
Disaccharide
Maltose
- two α-glucose molecules held by α 1–4 glycosidic linkage
Sucrose
-α-glucose and α-fructose with α 1–2 glycosidic linkage
Lactose
- α glucose and -α galactose
Polysaccharide
-complex carbohydrates
-hundred to thousand monosaccharide subunits
-held by glycosidic linkages
Function as
Energy Storage
Stored form of glucose
Starch
-plants
Is a combination of
Amylose
-straight chain polymer
-α-glucose with α 1–4 glycosidic linkages
Amylopectin
-branched-chain polymer
-α-glucose polymer with α 1–4 linkages in the main chain and α 1–6 linkages at the branch points
Glycogen
-animals
-similar to amylopectin in structure
-α 1–4 main chain linkages and α 1–6 branch-point linkages
-has more branches in glycogen
-animals possess enzymes that hydrolyze amylose and amylopectin
Structural Support
Provides structural support in
Cellulose
-major component of plant cell walls
-straight-chain polymer
-β-glucose held by β 1–4 glycosidic linkages
-humans are unable to digest the linkages between the β -glucose subunits in cellulose
Chitin
-hard exoskeleton of insects and of crustacean
-a cellulose-like polymer of N-acetylglucosamine
DNA
Deoxyribose sugar
-lack of an oxygen atom at carbon 2 in deoxyribose
-contains five carbons that
has lost the -OH (hydroxyl group)
on its 2 prime carbon
Three main components
Phosphate group that is
negatively charged
Nitrogenous base
Dextran
- held by 1-6 glucoside links
-the main chain of glucose has short branches
-joined by 1-3 and 1-4 glucoside links.
-structural component of bacteria and yeast