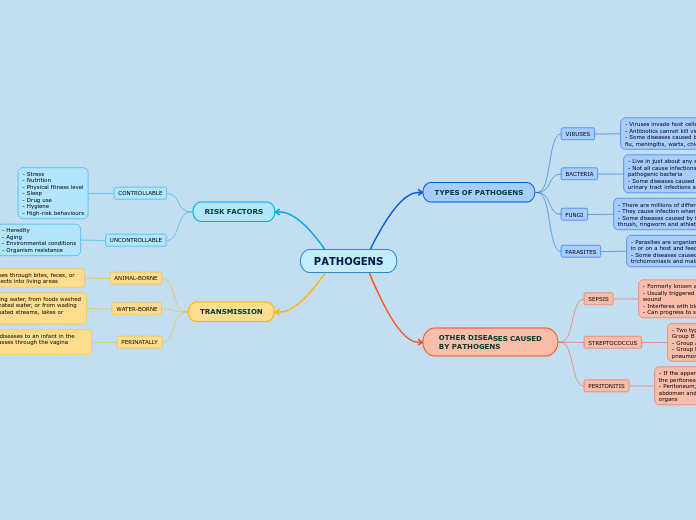
PATHOGENS
TYPES OF PATHOGENS
VIRUSES
- Viruses invade host cells within your body when infected
- Antibiotics cannot kill viruses
- Some diseases caused by viruses include the common cold, flu, meningitis, warts, chicken pox/shingles and measles
BACTERIA
- Live in just about any environment, i.e. human, body
- Not all cause infections, but those that do are called pathogenic bacteria
- Some diseases caused by bacteria includes strep throat, urinary tract infections and bacterial meningitis
FUNGI
- There are millions of different fungal species on Earth
- They cause infection when they overgrow
- Some diseases caused by fungi includes yeast infections, thrush, ringworm and athlete's foot
PARASITES
- Parasites are organisms that behave like tiny animals, living in or on a host and feeding from or at the expense of the host
- Some diseases caused by parasites includes giardiasis, trichomoniasis and malaria
OTHER DISEASES CAUSED
BY PATHOGENS
SEPSIS
- Formerly known as blood poisoning
- Usually triggered by a local infection such as pneumonia or a wound
- Interferes with blood flow
- Can progress to septic shock, and eventually death
STREPTOCOCCUS
- Two types cause infection in most people; Group A Strep and Group B Strep
- Group A Strep: strep throat, scarlet fever, etc.
- Group B Strep: In infants, can cause blood infections, pneumonia, meningitis
PERITONITIS
- If the appendix ruptures, the infectious material will spill into the peritoneal cavity and cause peritonitis
- Peritoneum, the tissue that lines the inner wall of the abdomen and covers and supports most of your abdominal organs
RISK FACTORS
CONTROLLABLE
- Stress
- Nutrition
- Physical fitness level
- Sleep
- Drug use
- Hygiene
- High-risk behaviours
UNCONTROLLABLE
- Heredity
- Aging
- Environmental conditions
- Organism resistance
TRANSMISSION
ANIMAL-BORNE
- Animals spread diseases through bites, feces, or by carrying infected insects into living areas
WATER-BORNE
- Transmitted from drinking water, from foods washed or sprayed with contaminated water, or from wading or swimming in contaminated streams, lakes or reservoirs
PERINATALLY
- Mothers can transmit diseases to an infant in the womb or as the baby passes through the vagina during birth