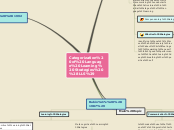
Categorization of Language Learning Strategies (LLS)
Oxford (1990)
Memory-related strategies
-Various memory related strategies enable
learners to learn and retrieve information in an orderly string (e.g., acronyms).
- memory strategies are often used for memorizing vocabular and structures in initial stages of language learning
Compensantory Strategies
- Example : guessing from the context in listening and reading, using synonyms,
help the learner make up for missing knowledge
Affective Strategies
identifying one's mood and anxiety level,about
feelings, rewarding oneself for good performance, and using deep breathing or positive self
Main topic
Stern (1992)
Management and Planning Strategies
Decide on suitable methodology,select proper resources and monitor progress
Set reasonable objectives
Decide what dedications to make tolanguage learning
figures
Cognitive Strategies
Gesturing,paraphrasing, or asking for repetition and explanation are methods employed by learners to keep the cobersation going
involve the use of verbal and nonverbal instruments for the useful transfer of knowledge
the purpose is to avoid interuupting the course of information
Interpersonal Strategies
monitor the learners' development and evaluate their performance
learners need to have communication with native speakers and cooperate with them
Rubin's (1987)
Learning Strategies
Cognitive Learning Strategies
involves direct analysis,synthesis, transformation of learning materials
Clarification,verification, guessing, inductive inferencing,deductive reasoning, practice, memorizatio and monitoring
Metacognitive Learning Strategies
are used to supervise, control or self-direct language learning
Planning, prioritizing, setting goals and and self-management
Communication Strategies
to make use of one's linguistic or communicative knowledge to remain in the conversation
Subtopic
Social Strategies
activities in which learners are opportunities that can be a great help to practice their knowledge