Cell Division & Cell Cycle
Mitosis
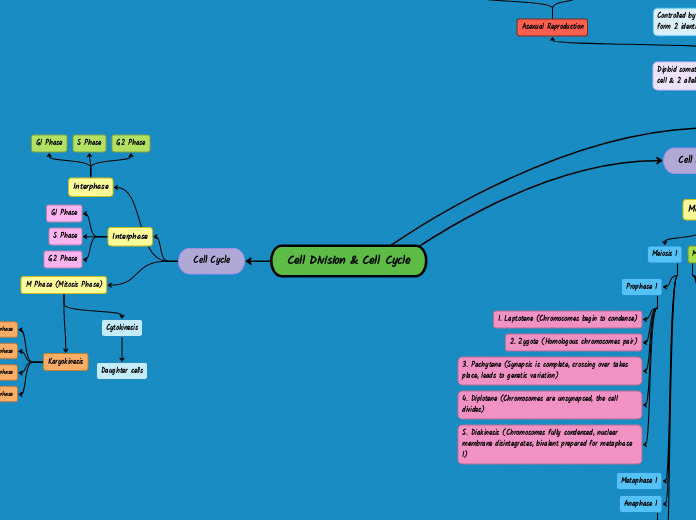
Diploid somatic cells (2 of each chromosome of a parent cell & 2 alleles)
Asexual Reproduction
Prokaryotic
Binary fission, DNA is copied & cells divide
Controlled by certain genes, cell duplicates & splits to form 2 identical daughter cells
Replacement Body Cells
Uncontrolled growth/copying = cancer, neurological disorders
Cell Division
Meiosis
Meiosis I
Prophase I
1. Laptotene (Chromosomes begin to condense)
2. Zygote (Homologous chromosomes pair)
3. Pachytene (Synapsis is complete, crossing over takes place, leads to genetic variation)
4. Diplotene (Chromosomes are unsynapsed, the cell divides)
5. Diakinesis (Chromosomes fully condensed, nuclear membrane disintegrates, bivalent prepared for metaphase I)
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Independent assortment occurs
Telophase I
Meiosis II
Prophase II
Metaphase ll
Anaphase ll
Telophase ll
Haploid gametes (1 of each chromosome of a parent (Germ) cell & one of a given allele)
Sexual Reproduction
Eukaryotic
Nondisjunction
Testes, ovaries & anther
Cell Cycle
Interphase
Gl Phase
S Phase
G2 Phase
Interphase
Gl Phase
S Phase
G2 Phase
M Phase (Mitosis Phase)
Karyokinesis
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
Daughter cells