The Great Depression of the 1930s

Stock Market Crash
During the 1920s, there was a sudden rush to invest in the stock market. With all the people investing in stock and making money, all the sudden everyone else wanted to get in on it. This caused many stocks to become overvalued, meaning they didn't accurately represent the value of the companies
Eventually, the investors realized how over valued the stocks were, and they all rapidly sold their shares. On Tuesday, October 29 1929, or Black Tuesday, the stock market crash, which caused many companies and individuals to lose all their money. This considered to be the start of the Great Depression.
Because many people didn't have much money to invest, they had to borrow it, meaning when the market crashed, all the money banks had lent out to people was lost as it couldn't be payed back. This meant that even if you didn't invest, the bank where you kept your savings may have failed and you would have lost all that money.
The Economy was in ruins.

Many people borrowed money they couldn't pay back.

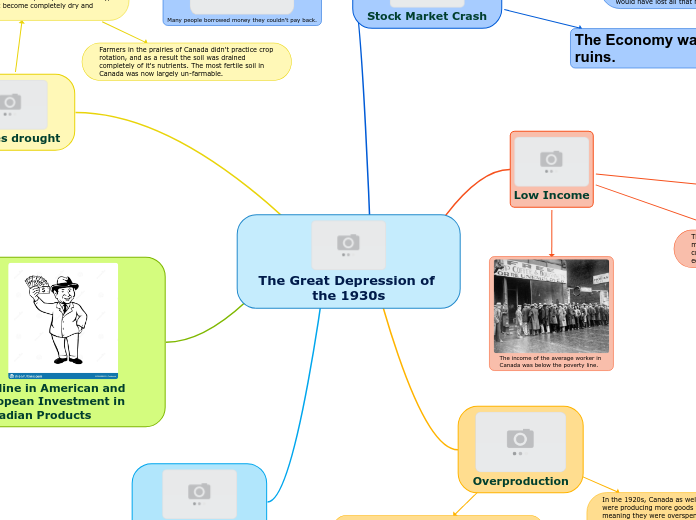
Low Income

The income of the average worker in
Canada was below the poverty line.
The didn't make enough money to survive, let alone enough to buy new technologies and invest. As a result, many people stated taking out loans they couldn't afford to pay off in order to buy the overproduced goods.
The buy now, pay later systems caused tens of millions of people to lose all their savings. They then couldn't afford to buy things, leading to more economic downturn.

Overproduction
Overproduction is when more goods are produced than there is a demand for,
Eg: More cars are produced than are bought.
In the 1920s, Canada as well as other countries, were producing more goods than they could sell, meaning they were overspending on materials, some of which had to be imported with tariffs, and weren't making the money back. Things like newspapers, wheat and cars were being way overproduced in Canada.
Because they had an excess, they had to start selling product as lower prices in order to get rid of them. This in turn caused companies to cut corners in other areas, mainly the salary of their workers. Many people were laid off and their wages dropped, leading to more economic downturn.

Prairies drought
From 1933 to 1939, on top of all the economic struggle, the prairies of Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba experienced a massive drought that in combination with over farmed soil made wheat production impossible.
Crop Rotation:
- When farmers plant different crops every 1-2 years to replenish the nutrients in the soil.
- Certain crops put a lot of nutrients back into the soil, while some take a lot out.
- Crop rotation is done to help keep the soil healthy, so the soil doesn't become completely dry and unusable.

These three crops; peanuts, soybeans and sweet potato's, replenish the soil with the most nutrients
Farmers in the prairies of Canada didn't practice crop rotation, and as a result the soil was drained completely of it's nutrients. The most fertile soil in Canada was now largely un-farmable.

Dust storms were very common during this period, and they blew away the top soil layer in what was now called the "Dust Bowl."

Decline in American and European Investment in Canadian Products
The American economy was unstable towards the end of the 20s, so Americans stopped investing in Canadian Products and taxed their imports to help save try and rescue their economy.
Europeans also stopped investing in products because their countries were in great debt after borrowing money from America for WW1, who were now going bankrupt.
In both cases, the countries stopped importing goods in order to stop unnecessary spending on tariffs and overpriced resources. For countries like Canada, who rely on exporting goods, this was terrible news.

Increased Tariffs

Tariffs are taxes that countries place on goods exported to other countries.
Eg: If the USA wants to import wood from Canada, they may have to pay an extra fee to take it from out country.
The problem with tariffs is if the material is ONLY available in another country and needs to be imported, or if your country does produce the material, but doesn't produce enough to satisfy the demand, than tariffs end up costing the country money.
Many countries add tariffs to things like lumber and metal so companies will buy the now cheaper local goods, instead of importing them. This helps to create jobs in said country, and makes the country less reliant on foreign imports.
The tariffs set forth in the 1920s were especially bad for Canada, as most of our GDP comes from exporting goods.