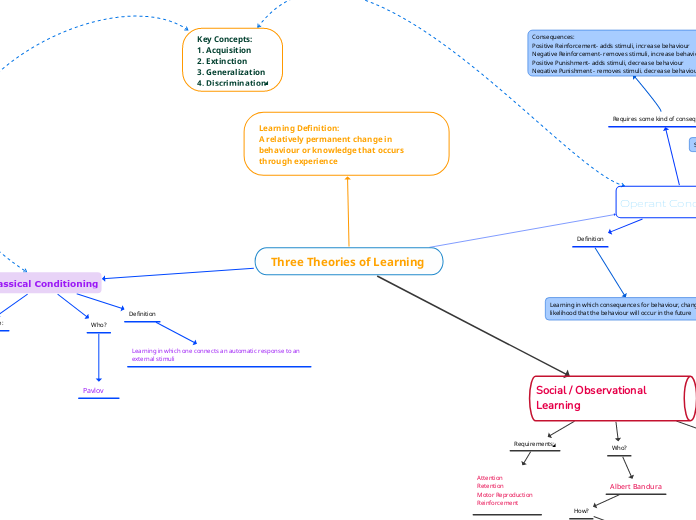
Three Theories of Learning
Classical Conditioning
Definition
Learning in which one connects an automatic response to an external stimuli
Who?
Must require:
Unconditioned Stimuli
Unconditioned Response
Conditioned Stimuli
Conditioned Response
Learning Definition:
A relatively permanent change in behaviour or knowledge that occurs through experience
Operant Conditioning
Skinners pigeons and rats
Schedule:
Fixed-Ratio
Variable- Ratio
Fixed Interval
Variable Interval
Partial Reinforcement - reinforcement for every occurence of the targeted behaviour
Continuous Reinforcement - reinforcement that is occasional or intermittent
Requires some kind of consequence
Definition
Learning in which consequences for behaviour, changes the
likelihood that the behaviour will occur in the future
Who?
John Watson
Social / Observational Learning
Definition
Who?
Albert Bandura
How?
Bobo Doll