u
Prenatal Testing
AMNIOCENTESIS
if a fetus has a particular genetic disorder
Down syndrome, sickle cell disease, cystic fibrosis etc
women who are at risk should get this procedure done
CHORIONIC VILLUS SAMPLING
doctor is removing a few cells from the developing placenta
NUCHAL TRANSLUCENCY SCREENING
measures the fluid at the back of a baby’s neck
GENETIC COUNSELLING
Understand what the results of these tests will mean for you and your family
DNA and RNA
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
final word in hereditary traits since it controls the structure of protein
depend on proteins called enzymes (ex: saliva)
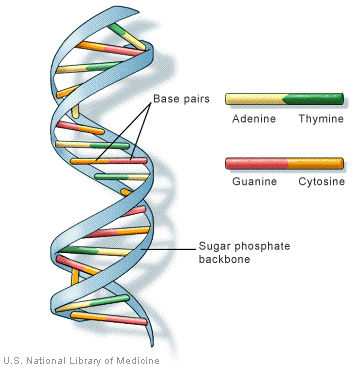
DNA structure
arranged in a ladder like structure called double helix
Nucleotides such as phosphate group, pentose sugar and nitrogenous bases
Nitrogenous bases form rungs
Adenine and thymine
Guanine and Cytosine
phosphate group and pentose sugar form a backbone in DNA
Codons are bases arranged in sequences of triplets
must be paired with the correct base bonds
Coding can change the entirety of an organism
DNA replication
each cell has a copy of DNA that is present in the zygote
DNA replicates its chromosomes through DNA replication
when two daughter cells duplicate, they must contain the same genetic information as a parent cell
DNA to protein
protein fold into 3D shapes and are key regulators
sequences of nucleotides in DNA contain information
are put to work through proteins

RNA (Ribonucleic acid)
RNA contains a replacement nitrogenous base thymine for URACIL (U)
Amino Acids is a type of protein
20 possible combinations of amino acids
20AA act like the alphabet
64 different combinations
production of proteins STOP and START codons
single strand of nucleotides and it occurs in a variety of lengths and shapes.
MRNA : is a type of RNA leaves the nucleus (VIA endoplasmic reticulum) with the code of protein
Nucleotides sequencing transcribed from DNA to mRNA, this is a genetic message
Mutations
caused by: errors throughout cell division, replication, transcription and external agents
Possibility on not passing to the offspring but can be dangerous for coming generations
Body cells and chromosomes
gamete cells
contains 1/2 number of chromosomes = haploid (n)
23+23=2N (46) a fertilize egg
Sex cell including sperm and Ova (egg) cells
ova located in the ovaries
During ovulation ovum is released and transported to the fallopian tube
sperm located in testes
homologues

homologue chromosomes
each position of the gene is in the same position as a homologue
homologues pairs (Tetrads) carry genes controlling an inherited trait
pair of chromosomes (maternal, paternal)
Karyotype is the display of human chromosomes
one homologue comes from the father and the other comes from the mother
somatic cells
contain a normal amount of chromosomes (46)
diploid # = 2N
body cells
skin cells, brain cells etc
Reproductive strategies
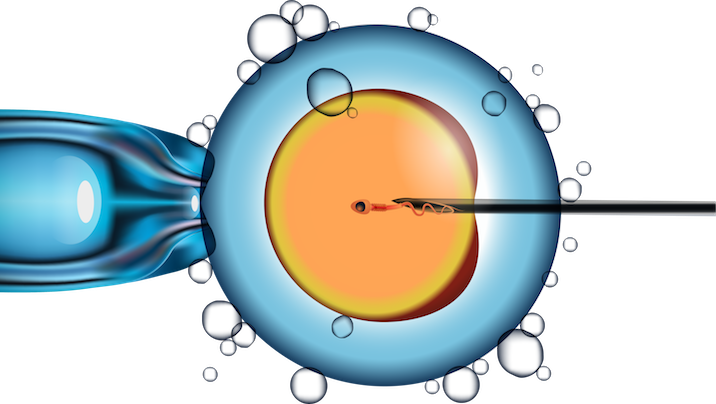
In vitro fertilization
used to fertilize an egg outside of the females body and egg combined in the laboratory with the sperm
therapeutic cloning
producing genetically identical cells to help treat diseases if needed
reproductive cloning
reproducing genetically identical organisms
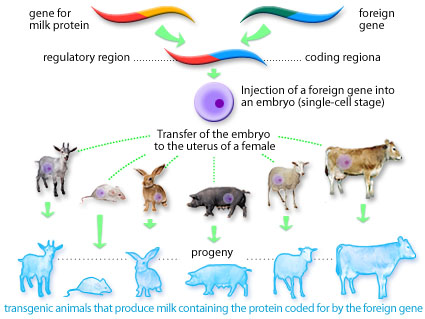
transgenic organisms
used to produce medical proteins or treatments
beneficial to our society in finding ways to prevent or to cure diseases
stem cells
are cells in our body that can specialize in different parts of our body
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis
procedure used prior detect any genetic disorders before implantation
Non-Disjunction: happens when chromosomes do not divide precisely
DOWN’S SYNDROME

a genetic mutation caused by an extra partial or full chromosome on the 21st set
TURNER’S SYNDROME
one of the X chromosomes is missing or altered
KLEINFELTER’S SYNDROME
there is an extra X chromosome for a male
Subtopic
Meiosis: is the production of gamete cells
Meiosis 1: will cross over genetic information between chromosome pairs + reduce chromosome number in half
interphase (preparation of meiosis)
chromosomes replicated (s phase)
duplicate chromosomes with 2 identical sister chromatids
Prophase 1
condensed
synapsed the process of homologue chromosomes creating a tetrad
Metaphase 1
shortest phase where independent assortment occurs
tetrads align on the interphase plate
genetic information is shared
Anaphase 1
homologue chromosomes split to each side of the poles
sister chromatids attach to the centromere
Telophase 1
each pole now has a haploid set of chromosomes
Meiosis 2: similar to mitosis (cell division)
Prophase (II) : preparing for the separation
metaphase (II): Sister chromatids are splitting apart from metaphase plate (II)
Anaphase (II): contracting to each poles
telophase (II): nuclei forms and cytokenesis occurs
In the end 4 haploid daughter cells are produced
Mendel and Inheritance
Monohybrid crosses - 1 trait crosses
complete dominance - one allele is not completely dominant
(blending of the 2)
incomplete dominance -neither alleles are dominant but are both expressed
produces a new phenotype
complete dominance is 1 allele is always dominant over the other
the law of segregation - 1 allele from each parent code - For ex: Yy
Dihybrid crosses - shows the possible offspring for 2 traits
mendelian ration 9:3:3:1
Mendel and the pea
beginning of learning about inheritance traits
the pea was a good observant since it was readily available and reproduction was controllable
study inheritance traits
homozygous/Pure inheritance
having the same alleles for a trait
Heterozygous/ hybrid inheritance
having 2 alleles (dominant and recessive) for a trait for
phenotype: the appearance of a trait in an organism
Genotype: genetic makeup of an organism
allele
Recessive alleles are represented by lower case
dominant alleles are descried using capital letter