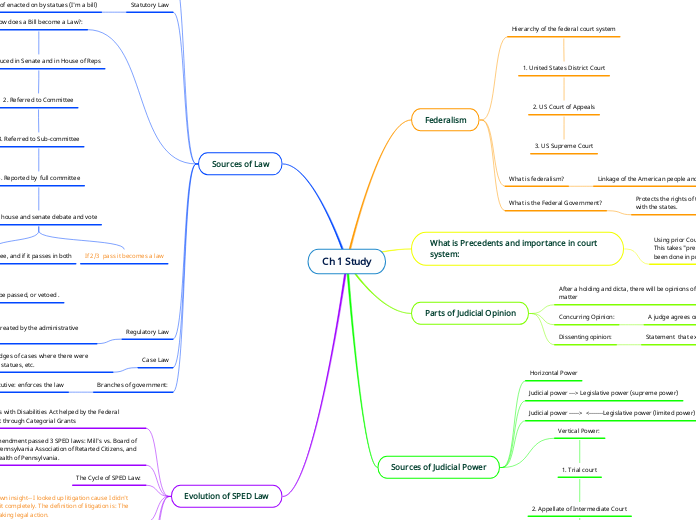
Ch 1 Study
Evolution of SPED Law
The cycle continues
Following Litigation is Legislation which is: Legislation: Own insight -- I looked up Legislation to help me define, and it said, "laws considered collectively", so in a way this is similar to precedence.
Litigation: Own insight-- I looked up litigation cause I didn't understand it completely. The definition of litigation is: The process of taking legal action.
The Cycle of SPED Law:
The 14th Amendment passed 3 SPED laws: Mill's vs. Board of Education, Pennsylvania Association of Retarted Citizens, and Common Wealth of Pennsylvania.
1. individuals with Disabilities Act helped by the Federal Government through Categorial Grants
2. Every Student Succeeds Act (Statutory law).
3. Smith vs. Robinson (handicap children) supreme courts decision.
Sources of Law
Branches of government:
Executive: enforces the law
Judicial Branch: creates law
Legislative: interprets the law
Case Law
Published opinions of Judges of cases where there were specific regulations and statues, etc.
Regulatory Law
Specific regulations for laws created by the administrative agencies.
How does a Bill become a Law?:
1. introduced in Senate and in House of Reps
2. Referred to Committee
3. Referred to Sub-committee
4. Reported by full committee
5. Both house and senate debate and vote
If 2/3 pass it becomes a law
6. Goes to Conference committee, and if it passes in both
goes to president and can be passed, or vetoed .
Statutory Law
Passed of enacted on by statues (I'm a bill)
Constitutional Law
Allocates responsibility among the legislative, judicial, and Executive branches of government. It defines their separation of powers.
Basic source of law in our legal system
Sources of Judicial Power
Vertical Power:
1. Trial court
2. Appellate of Intermediate Court
3. Court of Last Resort.
Judicial power -----> <-------Legislative power (limited power)
Judicial power ---> Legislative power (supreme power)
Horizontal Power
Parts of Judicial Opinion
Dissenting opinion:
Statement that explains why the judge doesn't agree
Concurring Opinion:
A judge agrees on a ruling, but not the reasoning behind it.
After a holding and dicta, there will be opinions of judicial matter
What is Precedents and importance in court system:
Using prior Court cases to make a ruling on a current case. This takes "precedence" over any other ruling because it has been done in previous cases.
I looked up some information about SPED cases and precedence and came across a website full of SPED cases that showed both 1. Appeals and 2. Decisions. Here's the website: https://specialeducationlawyernj.com/special-education-law/landmark-cases-in-special-education-law/
Federalism
What is the Federal Government?
Protects the rights of the people, while also sharing the power with the states.
What is federalism?
Linkage of the American people and communities.
Hierarchy of the federal court system
1. United States District Court
2. US Court of Appeals
3. US Supreme Court