Psychedelics
Eating
Usually how mushrooms-"shrooms" are ingested
Swallowed or dissolved on the tonugue
Usually how LSD is ingested
Liquid on a small square paper or on a microdot tablet
Also known as a "Blotter paper"
Powdered form
Denver, CO is the first city to support the decriminalization of psychedelics
Federally illegal
LSD and Psilocybin (forms of psychedelics) are considered schedule I drugs
High potential for abuse
Seizure disorder
Nightmares
Flashbacks
Visual distortions
Distorted sense of time/space
Enhanced emotion/empathy
Suggestibility
Trust
Closeness to others
Indoles and catechols
Subclass of hallucinogens
Mimic psychosis
Hallucinations begin to occur
Once ingested, psychedelics enhance sensory perception, thought processes, energy levels, thought processes
They do this by altering the chemicals in the brain through stimulating or suppressing neurotransmitters that are of the same chemical composition
Pain perception, responses to environment, emotion, learning and memory are impaired due to chemical imbalances in the brain
Currently being examined for medical benefits
Clinically-1950-1970
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Recreationally-used illegally
Constant hallucinations
Hallucinogen Persisting Perception Disorder(HPPD)
Specifically associated with use of LSD
Visual problem
Sometimes blindness
Vascular problems
Weakness
Increased blood pressure/heart rate
Ingestible papers
Usually in the form of acid
Pills
Ecstacy
Mushrooms
Contains psilocybin
Powdered or liquid
LSD
Also known as "acid"
Opioids
https://www.drugrehab.com/addiction/prescription-drugs/opioids/effects/
https://www.projectknow.com/opiate/effects/
https://www.quebec.ca/en/health/advice-and-prevention/alcohol-drugs-gambling/risks-of-opioid-use/
https://teens.drugabuse.gov/blog/post/real-teens-ask-what-are-different-types-opioids-0
https://www.ashclinicalnews.org/online-exclusives/new-federal-regulation-limits-amount-opioids-drug-companies-can-produce/
https://www.pharmacytimes.com/publications/issue/2011/june2011/an-overview-of-opioids
Fully synthetic
Fully synthetic opiates include:
Dextropropoxyphene
Tramadol
Levorphanol
Pethidine
Completely made by man
Semi synthetic
Semi synthetic opiates include
Heroin-derived from morphine
Created in labs from natural opiates
Natural opiates-alkaloids
Natural opiates include:
Thebaine
Chemical compounds are derived from a plant-opium poppy is an example
Many prescription/pain relieving medications containing opioids
Hydromorphone
Clinically
Pain alleviation
Anesthesia
Cough
For diarrhea
DEA enacted a new regulation requiring that opioid production will be cut by 1/5-20%
Estimates of opioids needed for medical use is determined to analyze the amount of opioids necessary to treat people without overproducing the drug
Hormonal issues
Muscle pain
Pneumonia
Irregular heart beat
Lethargy
Diizziness
Constipation
Feeling of excitement
Euphoria
Enzymes in the body convert opioids to morphine
Helps to relieve pain
Opioids attach onto receptors in the central nervous system
Peripheral tissues
Spinal cord
Brain
Schedule I drug
High potential for abuse and no medical benefits
Recreational
Schedule II Drug
High potential for abuse and can lead to physical/psychological dependence
Prescription
Morphine
Oxcodone
Hydrocodone
Opioids with mixed receptor actions
Butorphanol
Buprenophene
Mild-moderate agonist
Hydropcodone
Oxycodone
Codeine
Strong agonist
Fentanyl
Methadone
Morphone
Opioids are their own classification of drug
Suppressed immune system
Osteoporosis
Possible infertility
Hyperalgesia
Sensitive to pain
Suicide
By overdose
Depressed respiration
Slower breathing
Impaired mental functioning
Death
Rectal insertion
Intramuscular
Drug absorbed in a muscle
Oral
Through nose or mouth
Sometimes requires more of the drug for the same effect
Subcutaneous
Drug absorbed under the skin
Spray paint(Inhalant)
https://luxury.rehabs.com/drug-abuse/classifications/
https://www.drugfreeworld.org/drugfacts/inhalants/effects.html
https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/inhalants/what-are-inhalants
https://americanaddictioncenters.org/inhalant-abuse/huffing-paint
Intoxication is a short phase which causes users to inhale mass amounts which can be lethal
Imporrtant to note that death can occur due to mass inhalation
Fatal injury
Accidents/DUII crashes
Choking
Inhaling vomit after using an inhalant
Coma
Fom the body shutting down most of but not all of the vital functions
Convulsions/seizures
Due to abnormal electrical discharges through the brain
Suffocation
Blocking air entering lungs using the bag over the head method
Asphyxiation
From rerrpeated inhaling causing lack of oxygen in the lungs
Inhaled chemicals are ingested and immediately begin to disperse throughout the body bloodstream
From there, the chemicals spread further towrds the brain and into organs
The user feels the effects of intoxication (resemble alcohol)
Inhalants are typically household or industrial products used for services without intentions of them being inhaled
Due to the chemicals in these products, when inhaled they often give the user psychoactive and mind altering effects
Comatose
Extremely confused
Very drowsy
Major headaches
Impaired coordination
Agitation
Lightheadedness
disinhibition
Depending on usage, you may feel stimulant effects followed by effects associated with the depressant-alcohol
Inhalant
Some states have imposed jail sanctions, fines, and treatment programs for those in possession of and responsible for distributing inhalants
Inhalants are not regulated under the controlled substances act, but some states have regulations restricting minors from purchasing products often used as inhalants
4 types of inhalants
Nitrites
Isobutyl nitrite
Isoamyl nitrite
Typically used for sexual enhancement
Gases
Propane tanks
Nitrous oxide
Chlorophorm
Arersols
Hair spray
Deodorant
Spray paint
Volatile solvents
Liquids that vaporize at room temperature
Felt tip markers
Glue
Gasoline
Paint thinners
Rashes
Apathy
Irregular/rapid heartbeat
Lack of coordination
Impaired cognition
Impaired vision and hearing
Loss of muscular strength
White matter abnormalities
Larger brain ventricles
Brain atrophy-specifically near the Cerebellum
Orally-through the mouth
Huffing
soaking a rag and placing into mouth to be absorbed
Inhaled through a paper or plastic bag
Spraying directly into mouth
Sniffing/snorting
Meth
https://www.verywellmind.com/how-is-methamphetamine-used-63459
https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/methamphetamine/how-methamphetamine-different-other-stimulants-such-cocaine
https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-8676/methamphetamine-oral/details
https://nadk.flinders.edu.au/kb/methamphetamines/general-methamphetamine-information/
Some ADHD medications contain methamphetamine
This is legal to use as long as it is used within the prescribed guidelines by the intended user
Meth is typically used just to get high, although that's not always the case
Organ failure
"Meth mouth"
HIV/AIDS
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B
Violent behavior
Confusion
Intense itching
Extreme weight loss
Common Forms
Crystal meth
Typically smoked or injected
Most potent form of meth
Transluecent-white in color
Also known as "Ice"
"Base"
Also known as "pure", "paste", "wax"
Usually injected but can also be swallowed
Higher potency and purity than powder
Oily/damp feel
White/yellow/brown in color
Powder
snorted/injected/swallowed
Can be formed into pills
least potent form of meth
Also known as speed
White/off-white
Desoxyn
Narcolespy
Obesity
ADHD
Psychological dependence
Damage to brain-alzheimers
Depression
Disorientation/confusion
panic/psychosis
nausea
Disturbed sleep patterns
Loss of appetite
Trouble sleeping
Weight loss
Nausea
Injected
Powdered drug is injected
Especially dangerous due to risk of HIV and other similar diseases
Swallowed (pills)
Was originally used for medical purposes, but can still be found in pill form and abused
Smoked
Most common form of abused meth
Can give you "meth mouth"-teeth corrosion
Snorted
Drug is in powder form
Can lead to sinus cavity damage
Chronic runny nose is an effect
Can be smoked, snorted, swallowed or injected
When meth enters the bloodstream and heads toward the brain
When meth reaches the brain, dopamine levels increase beyond what is typical
Due to the way our brain processes this feeling, a reward system is implemented and makes the user want more and more of the drug
The FDA regulates meth that is used in medications to aid in treating ADHD, narcolepsy and severe obesity
Dispensed under the name "desoxyn" and manufactured by Ovation Pharmaceaticals
Recreational use of meth is illegal
Tobacco
https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/recognize-tobacco-its-many-forms
http://www.cesar.umd.edu/cesar/drugs/tobacco.asp
https://www.mydr.com.au/addictions/smoking-what-are-the-effects
https://www.pinerest.org/addiction/alcohol-drug-classifications/#Tobacco
Subtopic
Regulated by FDA (started in 2009)
HOWEVER: Military ages 18+ are allowed to purchase tobacco(and alcohol)
Laws vary state to state
Must have a state issued ID and be 21+ years old to purchase (in Oregon-other states may have a required age of 18 to purchase)
Used to be able to purchase at age 18, but the legal age has since been raised to 21 (11/50 states)
The following states have imposed the "21+ to buy tobacco" law
Virginia
Utah
New Jersey
Illinois
Hawaii
Arkansas
psychological dependence on the drug
Tolerance
Emphyzema
Chronic bronchitis
COPD
Damage to mouth
"Nicsick"- overdose of tobacco
Yellowing teeth
Gross smelly hair/clothes
Bad breath
(temporary) bronchitis
Damage to respiratory system
Feeling relaxed
Increased blood pressure and heart rate
Mild euphoria
Increased alertness/concentrration
Calm-followed by depression
e
Bronchitis
Cancer
Tooth decay
Gum disease
Nicotine from the tobacco is absorbed into bloodstream
Increases in dopamine
Rewarding behaviors
Adrenal glands are stimulated and epinephrin is released throughout the body
Responsible for increasing breathing, heart rat
How it's used
Tobacco isn't a medical or recreationsal drugs, however there are regulations regarding who is able to buy this drug
This varies state by state
Common forms
Smokeless tobacco
Usually place product between cheek and gums
Moist snuff
Powdered tobacco
Finely cut tobacco
Chew/dip
Cured tobacco-loose leaf/plug/twist
Dissolvables
Lozenges
Sticks
Strips
Electronic Cigarettes
Hookah pens
Vape pens
Cigars
Sometimes flavored-geared towards kids
Cigarettes
Most common
ORAL
Food(less common)
Chew
Sniff
Smoke
Increased heart rate and blood pressure
Relaxed
Increased alertness
Caffeine
https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-979/caffeine
https://healthfully.com/447204-fda-regulations-for-caffeine.html
Sources/Common Forms
Can be drank, eaten or swallowed in the form of medication/dietary supplements
Dietary supplements
Medications
Dark Chocolate
Drinks
Energy Drinks
Matcha green tea
Soda
Plants
Guarana berries
Yerba Maté
Coffee beans
Tea leaves
Kola nuts
Cocoa brans
Can lead to dependency issues
The more caffeine your body is used to, the more that is needed to produce the same effect (tolerance building)
However, NOT considered to be an addiction
Not many harmful long term effects oi caffeine
Different effects on different ages, genders, etc.
Youth (<100mg caffeine)
Pregnant women(<200mg caffeine)
Caffeine isn't the worst drug, and doesn't have horrible side effects
Caffeine overdoses
Feeling of intoxication (through excessive amounts o caffeine)
Symptoms
Insomnia
Irritability
Patterns of use
Up to 400mg of caffeine/day is safe for adults
Which equates to roughly 4 cups of coffee
Some Religions don't condone the consumption of caffeine
Blood vessels constricting
Slower blood flow in the stomach area
Muscle contractions
excessive caffeine intake causes
Increase blood pressure
Frequent urination
Nervousness
Fast heart rate
Tremors
How it works
increases the amount of calcium within cells
Caffeine enters the brain and binds to adosine receptions responsible for telling us we're tired
Increases calcium count within cells
Helps us to feel alert
Caffeine blocks the receptions from being able to communicate with the body, making us feel energized and not tired(until the caffeine wares off)
Increases dopamine levels
Makes us "feel good"
Allert
Dehydration
Higher body temperature
Feeling awake/energized
Uses/Effects
Breathing problems
Low blood pressure after eating
Athletic Performance
Asthma
Mental alterness
Weight Loss
Restore mental alterness
Alcohol containing caffeine has been banned
drugs containing caffeine must show they're safe and logical for human consumption
If the FDA approves, the amount of caffeine in the drug must be listed
Federal regulations state that products containing caffeine must contain no more than .02% of the actual product
Caffeine must be listed as an ingredient, but amount is not required
Not regulated
In fact, caffeine is on of the most common "addictive drugs"
Alcohol
concerns
Frequent intoxication
Substance Abuse
Harmful for brain development
Mixing with drugs
DUII
Dependence
Common forms-by percentage
Hard liquor
Tequila (40% alcohol)
Rum (35-45% alcohol)
Gin (37-47% alcohol)
Vodka (40% alcohol)
Whiskey (35-40% alcohol)
Wine (8-15% alcohol)
White wine
5-14.5 % alcohol
Chardonnay
Pinot Grigio
Moscato
Red wine
12-15% alcohol
Red bordeauxs
Malbec
Pinot noirs
Beer (2-6% alcohol)
Porter
Pale ale
Lager
Stout
Ale
Slower respiration
Loss of coordination
Loss of Inhibitions
Drink it
Socializing
Relaxation
Wear it
Alcohol used in perfumes
Ethanol used to dissolve things
Vegetable essences
Sources:
https://www.drugfreeworld.org/drugfacts/marijuana/short-and-long-term-effects.html
http://www.alcoholandyou.org.uk/facts/uses.html
https://www.drugrehab.com/addiction/drugs/marijuana/what-kind-of-drug-is-marijuana/
https://www.drugfreeworld.org/drugfacts/alcohol/short-term-long-term-effects.html
https://www.andygreenlaw.com/general/alcohol-volume-popular-whiskeys-vodka-gin-rum/
https://www.pinerest.org/addiction/alcohol-drug-classifications/#Alcohol
Vanilla extract
Cosmetics
Perfume
Burn it
Ethanol can be used as an alternative to fossil fuels
Clean with it
Ethanol +methanol to clean paint brushes
Brain damage (permanent)
Ulcers
High blood pressure
Liver disease
Alcohol poisoning
Unintentional injuries
car crash
Impaired judgement
Unconsciousness
Increased aggression
Decreased heart rate
Headaches
Upset stomach
Vomiting
Drowsiness
Slurred speech
Regulations
Must be 21 to purchase
Ingestion through drinking
Alcohol impacts people differently based on age, sex, weight, and food consumption
After alcohol is consumed, it moves through the body and into. your bloodstream. Effects cane felt
After alcohol is in the bloodstream, it passes the blood brain barrier which inhibits brain functioning
Finally, the liver breaks down the alcohol and it is prepared to go through our system
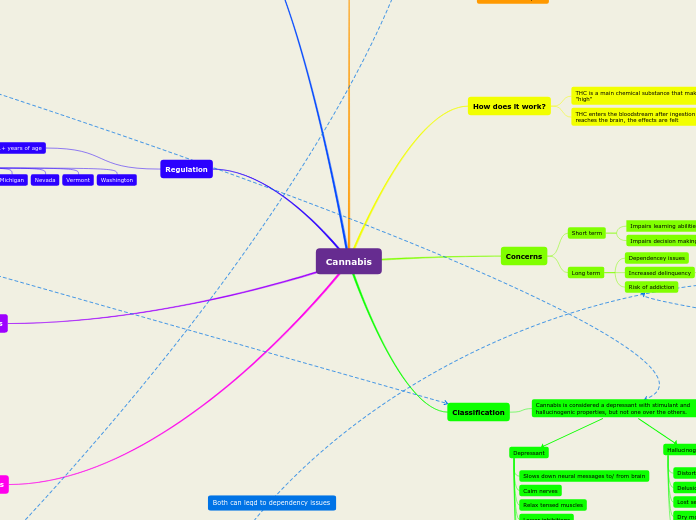
Cannabis
Common Forms
Flower/ bud
THC levels orange from low to high potency depending on strains
Oil (also known as dabs or extracts)
Has high THC levels are found in this form of cannabis. Oils from the cannabis plant are extracted to make dabs.
Effects
Antisocial behaviors
Less job opportunities
Little satisfaction with life
Poor school/work performance
Relationship issues
Addiction
Decline in IQ
Lower reaction times
Loss of personal identity
Hallucinations
Anxiety
Short term memory issues
Regulation
Cannabis is fully legal in 10 states for users 21+ years of age
Washington
Vermont
Nevada
Michigan
Massasschusettes
Maine
Oregon
Colorado
California
Alaska
How is it used?
Can be used medicinally or recreationally
Dab pens
Cannabis can be ingested through eating edibles/drinking. beverages
Liquid Items
Syrup
Lemonade
Food Items
Chocolate
Taffy
Cereal Bars
Brownies
Cookies
Cannabis is most frequently smoked
Other makeshift devices
Soda bottles
Fruits
Dab rigs
Pipes
Blunts/joints
Bongs
Classification
Cannabis is considered a depressant with stimulant and hallucinogenic properties, but not one over the others.
Hallucinogen
Detachment from self
Dry mouth
Lost sense of personal identity
Delusions
Distort users perception of reality
Stimulant
Paranoia
Elevated mood
More attentive
Increased heart rate
Increased alterness
Depressant
Short term memory loss
Dizziness
Sleepiness
Lower inhibitions
Relax tensed muscles
Calm nerves
Slows down neural messages to/ from brain
Concerns
Long term
Risk of addiction
Increased delinquency
Pathway to use of other drugs
Dependencey issues
Short term
Impairs decision making skills
Bad. judgement
Impairs learning abilities
Grades suffer
How does it work?
THC enters the bloodstream after ingestion and once it reaches the brain, the effects are felt
THC is a main chemical substance that makes someone feel "high"
Routes of administration
Electronic consumption
Eating edibles/ drinking beverages
Vaporizing