Human Energy Systems and Muscle Fibres
ATP
-adenosine triphosphate
-energy currency of the human body
- allows for the muscles in the body to contract, producing movement
1 molecule of ATP is produced in ATP-PC
2 molecules of ATP are produced in glycolysis
36 molecules of ATP are produced in cellular respiration
3 Metabolic Pathaways
Cellular Respiration (aerobic)
examples would be a marathon or a soccer match
over two minutes of activity
36 molecules ATP produced/ molecule glucose
through various metabolic pathways in the mitochondria
refers to the process in which body's cell use oxygen to generate energy
Glycolysis (anaerobic lactic)
examples are speed skating, medium distance track events, and a shift in hockey
yeilds to ATP/ glucose molecule
lactic acid is produced in the abscence of oxygen, creating a burning feeling in the muscle
high level of performance for 100 seconds
second anaerobic pathway
allows longer bursts of energy
doesnt involve oxygen (anaerobic)
lactic acid is a byproduct
partial breakdown of glucose
ATP-PC (anaerobic alactic)
examples are weightlifting, 100m sprint, and shot put
Yields enough ATP for 10-15 seconds of strenuous activity
First of 2 anaerobic systems
Relies on the action of phosphocreatine (compound normally stored in muscle)
"alactic" does not produce lactic acid as a byproduct
Allows for quick, intense muscle contractions
Draws on processes deep within the muscle fibre
Energy Sources
Glycogen, fats and proteins
they are broken down to produce ATP during exerzise
provides energy during exercise for a prolonged period of time
used as an energy source for the Aerobic Lactic system
Glucose
broken down into pyruvate, which is then converted to lactate
provides energy quickly
used as an energy source for Anaerobic Lactic system
Creatine Phosphate
provides quick short lasting energy.
Used as an energy source for the Anaerobic Alactic system
Myoglobin
fast twitch (pale) muscle fibres are low in myoglobin and more adapted to short bursts of energy
slow twitch (red) muscle fibres are high in myoglobin and ideal for endurance
a protein oxygen storage unit that delivers oxygen to the muscles
Muscle Fibre Types
fast twitch:
pale in color
can tense and relax quickly
generates large amounts of tension with low endurance levels
type 2b
high level of enzymes necessary for quick contraction
stores lots of oxygen (without requiring oxygen)
type 2a
allows high speed energy release and glycolytic capacity
interediate type muscle fibres
slow twitch:
red/dark in color
generate and relax tension slowly
maintains low tension level for long periods of time
ex. long distance running
type 1
depends on aerobic processes
more fatigue resistance
generates energy slowly
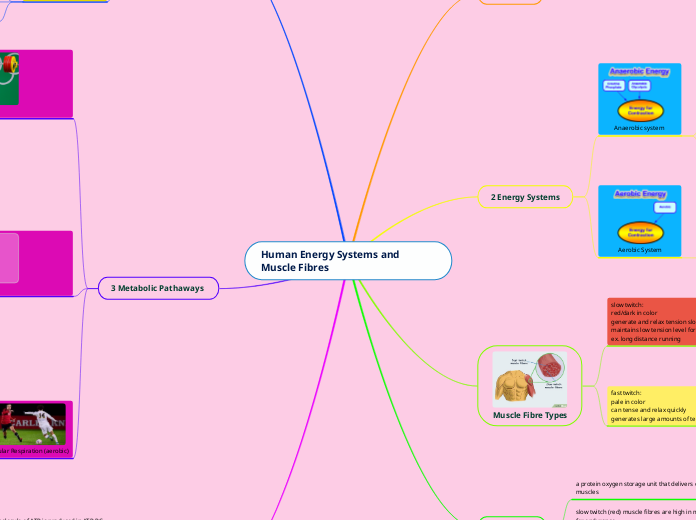
2 Energy Systems
Aerobic System
Aerobic System (Cellular Respiration)
-Involves many enzynes and several complex sub-pathways (leads to the complete breakdown of glucose)
-A seperate but to some extent overlapping energy system
-With oxygen (required).
Anaerobic system
Anaerobic lactic (glycolysis)
Anaerocic Alactic (ATP-PC)
- Without oxygen (not required).
- Can occur in two seperate metabolic pathaways (1 involving the breakdown of glucose and the other a partial breakdown)
Nutrients
chemical substances obtained from food
three key energy nutrients are carbohydrates proteins and fats, with carbs being the most important
needed to obtain energy for survival
body requires nutrients to perform life functions
builds and repairs tissue
regulates cellular activities
supplies energy to the body