по Qabas Al-Jobori 1 года назад
159
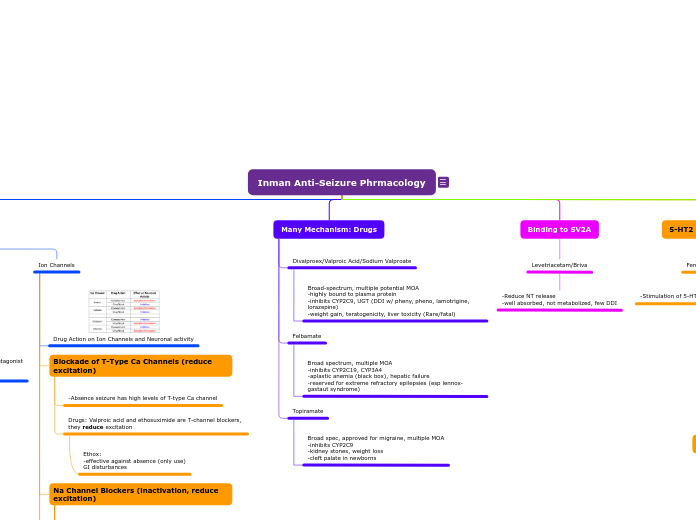
Inman Anti-Seizure Phrmacology
по Qabas Al-Jobori 1 года назад
159

Больше похоже на это
ride rollercoasters in the Top Zone amusement park to pass kidney stones
Ane felt too Feeble to play with her Plastic Car
Aplastic Anemia --> felbamate + carba
Val got in the Car 🚗--> accident --> lost her baby --> teratogenic
Val Gambled & got Pregnant 🤰 (i.e. gained weight)
gonna find me a Top Zaddy once I lose weight
Steven & Johnson are Lame Barbs
Can Phineas & Ferb be Hip (Hepato) Victorious Vigilantes
Can't Escape Overwatering = water retention = hyponatremia
Drugs: Gaba/pregaba
Pregabalin 3-10x more potent -does NOT mimic GABA effects -not metabolized, not bound to protein, no DDI, well tolerated -weight gain
Ezogabine: -adj + alt for partial seizure Unique MOA: Neuronal KCNQ/Kv7 K channel opener
ADE: QT prolongation, blue skin discoloration, retina pigment changes
Other drugs: Primadone (not much to say)
Zonisamide: -works on both Na/T-type Ca channels -Kidney stones, weight loss, oligohidrosis
Rufinamide: -When all else fails, use this May increase convulsion in some pts.
Phenytoin/Fosphenytoin: -narrow therapeutic window -Gingival hyperplasia -skin thickening; hirsutism; acne
Lamotrigine: -1st/2nd line for most seizures, broad spectrum -metabolism inhibited by UGT (DDI valproate) -Stevens-Johnson syndrome/rash
Lacosamide: -1st line partial seizures -Class V controlled
MOA: Slow recovery of voltage-gated Na Channels in neurons
-Iminostilbenes (zepines)
Oxca/Eslic: good/complete oral absorption -hyponatremia -less potent inducer of liver enzymes/no autoinduction
Carba: slow/erratic oral absorption -autoinducer (aka it induces its own metabolism = lower blood conc. at higher doses) -Asplastic anemia, leukopenia, hepatic toxicity, teratogenicity, hyponatremia
Drugs: Valproic acid and ethosuximide are T-channel blockers, they reduce excitation
Ethox: -effective against absence (only use) GI disturbances
-Absence seizure has high levels of T-type Ca channel
Drug: Perampanel - Glutamate/AMPA receptor antagonist -90% protein bound, many DDI -Partial + generalized seizures
Activation leads to: -inc influx of Ca/Na -member depolarization -encourages generation of action potential
GABAergic Agents
Stiripentol: only used as adj for driver syndrome w/ clobazam
Vigabatrin: -1st line for infantile spasm, adj for partial seizures -may aggravate seizures + psychiatric effects in pts. w/ depression, psychosis -progressively reduces visual field in high % of pts, hepatotoxicity
Tiagabine: -95% protein bound -inc incidence of seizures and status epileptics
Phenobarbital/Primadone (also Na blocker)
Pheno: -has the least sedative effect in its class -long half-life (5 days), induces CYP/UGT -v strong sedation, cog impairment, behavioral changes -hepatotoxicity, SJS, toxic epidermal necrolysis, risk of dependence
BZDs: Clobazam, Clonazepam, Diazepam, Lorazepam -Reserved for emergency due to tolerance -MOA: Positive allosteric modulators of GABA-A, increase freq of GABA-Activated Cl channel opening
Lorazepam/diazepam 1st line for status epileptics (IV) -Abrupt DC of clobazam may cause withdrawal symptoms (convulsions, psychosis, hallucinations, anxiety, tremor)
GABA-A is a Cl channel -Activation inhibits the action potential