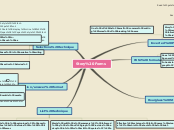
Story Forms
List technique
Effective technique for news releases, which should be brief.
Starts with a summary, followed by a nut graph. Provides backup info for with quotes, fact or both.
Limit lists in beginnings & middles of stories to 5 items or fewer.
Works for studies about stories: government stories such as meetings
Question/answer format
Is very useful for mobile media stories
Good technique for print and web stories
Organizes stories by questions and answers
go over the map
put your mind to work
recall as many details as you can about the keywords you added
Selections technique
Has two different section stories for organizing it
Times frames
Points of view
Often used in narrative writing
make info
easier to remember
interesting
save time
Works best for in-depth stories such as
Mobile media devices
Web pages
Investigation or long features
Involves dividing story into sections
Hourglass Structure
Useful for crime or disaster stories
Used when story has a dramatic action that lends itself to a chronological order
Disadvantage
May repeat some key info in the top of the story
Advantage
Narrative storytelling in chronological portion adds drama to story
Can start as an inverted pyramid, but it covers stories in a chronological way
Has more like a sand watch structure
WSJ formula
Introductory paragraph, backup paragraph, finally quote or anecdote
Goes from the specific to the general news
Inverted Pyramid
Story is structured with the most important info. at the top, followed by supporting points in order of importance.
Disadvantages
Reader may not read past important information
Advantages
Read gets important information fast
One of the most common writing forms of breaking news