по Nathalia Moncayo Ramirez 10 месяца назад
45
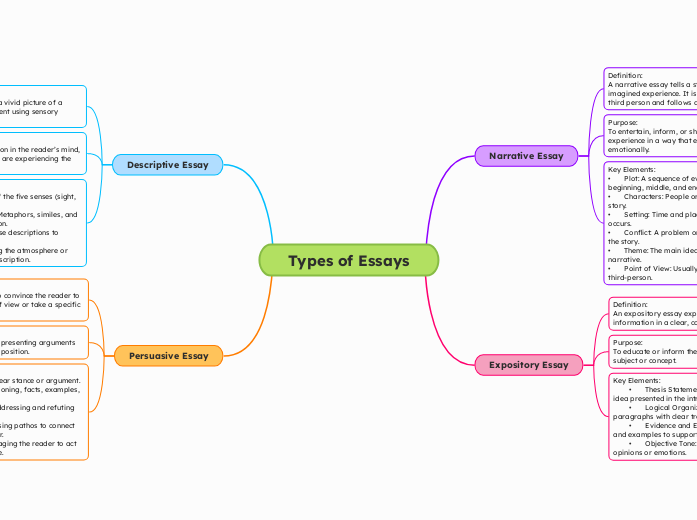
Types of Essays
Essays come in various forms, each serving a unique purpose. A persuasive essay aims to convince the reader of a particular viewpoint through logical arguments, evidence, and emotional appeals.