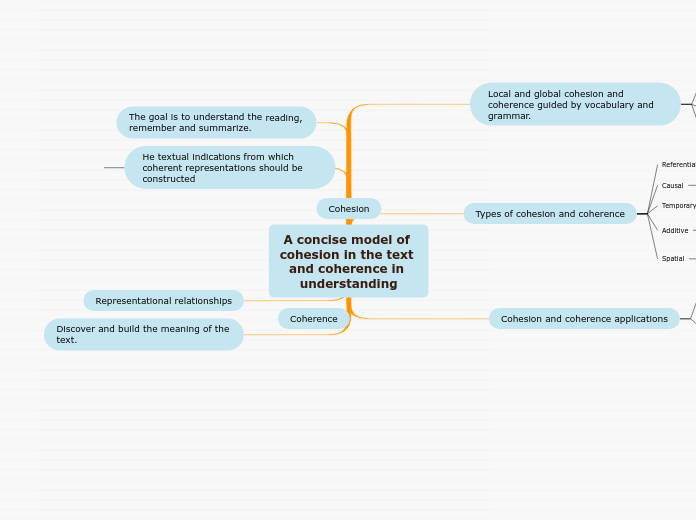
A concise model of cohesion in the text and coherence in understanding
Local and global cohesion and coherence guided by vocabulary and grammar.
Grammar-driven cohesion can occur alongside vocabulary-driven cohesion, and it has been argued that both interact in the emergence of coherence.
Can be described in terms of micro and macrostructures.
Local cohesion joins adjacent textual units, while global cohesion joins larger chunks of textual units.
Types of cohesion and coherence
Referential
consists of that or that to whom reference is made, often indicated by anaphora.
Causal
Facts of two sentences that are related.
Temporary
Time in which certain events occur and often signaled by the verb tense.
Additive
Unspecified information between events related to the addition.
Spatial
Consistency in which events occur marked by adverbial phrases or points of view. Events are spatially cohesive if they share the same place.
Cohesion and coherence applications
More recently, McNamara, Louwerse and Graesser
Theories, evidence and applications of cohesion and coherence.
Its objective was not to provide a complete picture, but to highlight some of the ongoing research in a range of interdisciplinary areas, including psycholinguistics, computational linguistics, corpus linguistics, and literary studiesnvestigating how cohesion affects coherence.