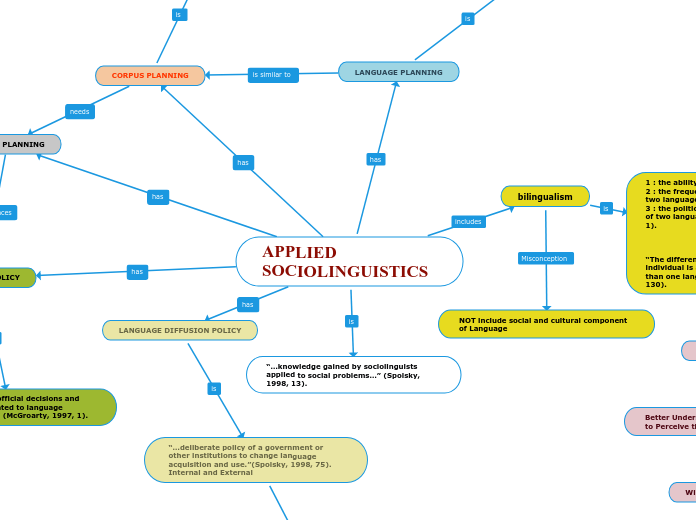
APPLIED SOCIOLINGUISTICS
LANGUAGE PLANNING
Any effort to modify language form or use / 1950s-1960s
Cooper: “…deliberate efforts to influence the behavior of others with respect to the acquisition, structural or functional allocation of their language codes.” (Cooper, 1989, 45).
bilingualism
1 : the ability to speak two languages
2 : the frequent use (as by a community) of two languages
3 : the political or institutional recognition of two languages.” (Merriam-Webster. n.d., 1).
“The different degrees in which an individual is able to communicate in more than one language or culture” (Usma, 2009, 130).
Foreign Language
Better Understanding of the Other / Ways to Perceive the World
Window to Human Mind
Second Language
Indigenous Language / Creole in San Andrés /Portuguese in the Amazonia
NOT include social and cultural component of Language
“…knowledge gained by sociolinguists applied to social problems…” (Spolsky, 1998, 13).
CORPUS PLANNING
“…any effort to modify the structure of a language…”(Spolsky, 1998, 66).
“When… the status of language is to be moved to a more elaborate level of standardization or to an expanded set of functions…”(Spolsky, 1998, 70).
“Corpus planning deals with norm selection and codification, as in the writing of grammars and the standardization of spelling; status planning deals with initial choice of language, including attitudes toward alternative languages and the political implications of various choices” (Bright, 1992, p. 311).
Technology
Use a new term or combine terms or borrow from another language
Orthography: Example: Turkey’s modernization (Ataturk) use of Roman alphabet
STATUS PLANNING
“… rules or norms when there are two or more languages are available…”(Spolsky, 1998, 66).
“A political activity” (Spolsky, 1998, 69).
Regulated by the country’s Constitution, laws, decrees
When a nation becomes independent: Example: India / Post-Colonial African Countries / New Zealand : Maori and English
Or a Nationalistic Movement like the Zionist Movement making Hebrew the Official Language.
A Religion like Catholicism which uses Latin as its Official Language
LANGUAGE DIFFUSION POLICY
“…deliberate policy of a government or other institutions to change language acquisition and use.”(Spolsky, 1998, 75).
Internal and External
Germany with the Goethe Institute / France with L’Alliance Française / Spain with the Instituto Cervantes
To spread influence, trade and tourism. Also governments direct the policies.
LANGUAGE POLICY
“… combination of official decisions and public practices related to language education and use.” (McGroarty, 1997, 1).
COLOMBIAN POLICIES
Ideal
Teacher Training Programs Beyond Language Acquisition
Eradicate Poverty
Reduce Inequalities
End the War Humanistic
Social Empowering
Liberating Education
First Fluency in Spanish
Include CLIL
Policy for Everyone in ALL Parts of the Country
Results
British Council and Cambridge University Press make profits
Indigenous languages are underestimated Mhuysqua
Ticuna
Exclude Indigenous Languages from Bilingualism
Negative effects on Ethnic Groups
Other Foreign Languages disregarded : Portuguese (In the Amazonia)
Not achieve goals set by the laws/programs
Lack of Continuity
Jobs instead of Social Development
Disown local traditions and languages
CEFR : NOT include differences between European and Colombian context
Teachers are NOT heard
Connected to Economic, Political and Cultural Agenda
Exclusion of Less Powerful Groups
“Elite Bilingualism”
Students have to: Meet a Standard / Pay for Tests / Be Certified Usma, J. (2009).
Bonilla, C.A. and Tejada-Sánchez, I. (2016).
Gómez Sará, M. M. (2017).
Why English?
Technology, Modernization, Economic Progress, Better Job Opportunities Usma , J. (2009).
Bonilla, C.A. and Tejada-Sánchez, I. (2016).
Gómez Sará, M. M. (2017).
LAWS
1826 : Spanish, Latin, Greek, French, English and an Indigenous Language
1970: No more Latin
1979: French
1989: British Council’s Report / Survey of English Language Teaching and Learning
NATIONAL CONSTITUTION: 1991
Decentralize
Lay State
Recognition of All Indigenous Languages
World Bank
World Trade Organization
International Monetary Fund
Law 115 of 1994: General Law of Education
“The capacity to use and understand a foreign language”
Little impact on Teachers’ Practice & Students’ Learning
Gap Between Private and Public
1997: COFE PROJECT ( Colombian Framework for English)
Teacher Professional Development
Material Resources
Research
Autonomy
Reality: Actual University Structures / Teacher’s Not Familiar with Research / Limited Resources
Law 1651 : 2004- 2016: English as the Lingua Franca
LAW of BILINGUISM: July 12, 2013
EDTDH need certificate of quality
Only hire certified teachers
Financing
NATIONAL PLAN of BILINGUISM: 2004-2019:
Completely change Foreign Language Teaching and Learning
Ethno-Education: Indigenous Languages
Flexible Models Of Education
Communicative Skills in English for schools and universities
Adopt CEFR / Standardize Foreign Language Teaching
Saber Exams : Asses in reading, vocabulary, grammar NOT speaking, listening, writing
Diagnostic Tests for Teachers / Quick Placement Test / TKT
NATIONAL BILINGUAL PROGRAM : 2005
Standards for English Teaching and Learning
Evaluate Communicative Competence of Students and Preservice Teacher
Professional Development
Technology
Different Ethnic Communities
DECREE 3870 : 2006
Common European Framework of Reference for Languages
PROGRAM for STRENGTHENING the DEVELOPMENT of COMPETENCES in FOREIGN LANGUAGES : 2010-2014
Emphasize English
Knowledge Economy
Training and Professional Development --- Teach English (Tests)
Pedagogical Aspects – Materials
BILINGUALISM LAW: 2013
English as a Technical Tool for Employment
NATIONAL PLAN of ENGLISH: COLOMBIA VERY WELL! : 2015-2025
Diagnosis and Training of Teachers
Public Schools: Increase hours of English
Technology / Tools / Materials BILINGUAL COLOMBIA : 2014- 2018
Open Focus to Other Languages
NATIONAL BILINGUAL PLAN: 2018-2022
MEN Web Page
Last Policy
Bonilla, C.A. and Tejada-Sánchez, I. (2016).
COMMON EUROPEAN FRAMEWORK of REFERENCE
Externalization of Policy Discourse
Instrumentalization of Languages
Inclusion, Exclusion, Stratification through Policy Transfer
Power and Control
“Knowledge Economy”
“Global Economy”
Free Trade Agreement Usma, J. (2009)
Subtopic
In the Classroom
Colombian Context
Varied Population
Infrastructure
Curriculum
SHORTAGE : Materials & Technological Resources
Teacher’s Language Proficiency
Number of Students per Class = OVERCROWDED
LIMITED : Number of Hours per week
NO Mobility Usma, J. (2009)
Real Life:
Low Socio-Economic Levels
SISBEN
Displacement because Internal War
Drugs
Gangsters
Insecurity
Prostitution
Poverty
Violence
Silence in the Classroom
Disconnect between Syllabus/Curriculum and Real Life Rincón & Clavijo-Olarte, (2016).
Community Based Pedagogies
Multimodality: Use of Technology and Social Networking Rincón & Clavijo-Olarte, (2016).