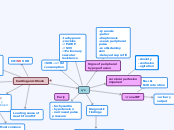
Cardiogenic Shock
either systolic or
diastolic dysfx of
the ♡'s pumping
action results in
⇓ CO(⇓ 4L/min)
⇓filling results in
⇓ SV
CO=SV X HR
systolic dysfx:
heart's inability
to pump the blood
forward
primarily affects
the LV
Most common
cause: MI
Leading cause of
death from MI
s/s
-tachycardia
-hypotension
-narrowed pulse
pressure
⇧SVR-->⇧ O2
consumption
-tachypneic
-crackles
-⇧ PAWP
-⇧ SVV
-⇧Pulmonary
vascular
resistance
Signs of peripheral
hypoperfusion
-cyanosis
-pallor
-diaphoresis
-weak peripheral
pulse
-cool & clammy
skin
-delayed cap refill
⇓ renal BF
Na+ &
H20 retention
⇓ urinary
output
cerebral perfusion
impaired
-Anxiety
-confusion
-agitation
Diagnostic
findings
⇧Cardiac markers
⇧b-type natriuretic
peptide(BNP)
⇧Blood glucose
⇧BUN
-ECG(e.g. dysrhythmias)
-Echocardiogram(e.g.left
ventricular dysfx)
-chest x-ray(e.g. pulmonary
infiltrates)