Climate
Weather vs Climate
Weather
Weather is defined as atmospheric conditions
in a particular location over a short peroid of time.
Weather includes things like temperature,
humidity, precipitation and wind.
Climate
Climate is the weather of a region over
a longer period of time, such as thirty years.
The weather of a place changes constantly
but the climate changes slowly over time.
The climate of a region also determines
the types of flora and fauna that live there.
Factors that affect climate
Distance from the equator ( Latitude)
The farther an area is from the equator, the cooler it is. On the other hand, the closer an area is from the equator, the warmer it is.
This is because The Sun's rays fall on the Earth in a diverging path. The places at the equator get direct light and the places far from the equator get more scattered light.
India is close to the equator and gets direct light. So, it is warmer than other places.
The North pole is far from the equator and gets divergent light rays. So, it is cooler than other places.
Presence of large bodies of water
Presence of large bodies of water gives a place humidity. Humidity then causes the place to be cooler as water heats and cools slower than land. So, places that are closer to the water are more cool in the summer.
Islands are cool as they are land masses that are completely surrounded by water.
places that are farther from water bodies are warmer than areas that are closer to water bodies.
Presence of ocean and air currents
Presence of ocean and air currents contributed to a place being cooler. As I previously stated, water warms and cools slower than land. So, wind currents that are over water get cooled and heated as the temperature of the water.
The air currents are then pushed towards land masses and they make the land mass warmer or cooler based on the temperatures they picked up from the water.
Land formations
The different landforms such as volcanoes, mountains etc have a great effect on the weather systems of the Earth.
High mountains are cooler than valleys. This is a good example to help understand why landforms affect the world's weather systems.
Height aboe sea level (altitude)
The height above sea level is a big factor in the climate of a place. Places that are higher have a cooler climate and places that are lower have a warmer climate.
The temperature usually drops at a rate of 1 degree celsius per 100 metres.
This is because the air gets less dense the higher you go. So, the molecules will be more spread out and less likely to collide.
The Earth's surface emits energy
As the Earth warms up it gains thermal energy
The thermal energy is converted into low energy infrared (IR) radiation.
The amount of energy radiated by the Earth's climate system is eqal to the amount of radiation the Earth absorbs from the Sun.
Because of this balance of energy the Earth's temeprature stays fairly constant.
Climate change
Climate change means that the Earth is getting much hotter than it used to be. A more common term for this is global warming.
The cause of global warming is that carbon dioxide and other green house gases are being mass produced in the world.
The cause for this is that we are destroying plants and trees and replacing them with factories that create greenhouse gases at a very high rate.
Beef as a problem for the climate
It produces more greenhouse gases per pund than any other type of meat. This is due to the presence of methane.
All cattle release methane as a bi-product of digestion.
Beef is the main cause for deforestation as a lot of and is needed to raise them.
Climate Zones
The system of classification of
climate zones is known as the
Koppen-Geiger classification system
The Koppen-Geigner climate classification system was first introduced by climatologist Wladimir Koppen (1846-1940) in 1884. He made some modifications to it in the years to come. Some later modifications were made by the climatologist Rudolf Geigner. Thus, it came to be known as the Koppen- Geigner Climate Classification system. (Source:Wikipedia)
The climate of a place is classified by letters.
A- Tropical
B- Dry
C- Temperate
D- Continental
E- Polar

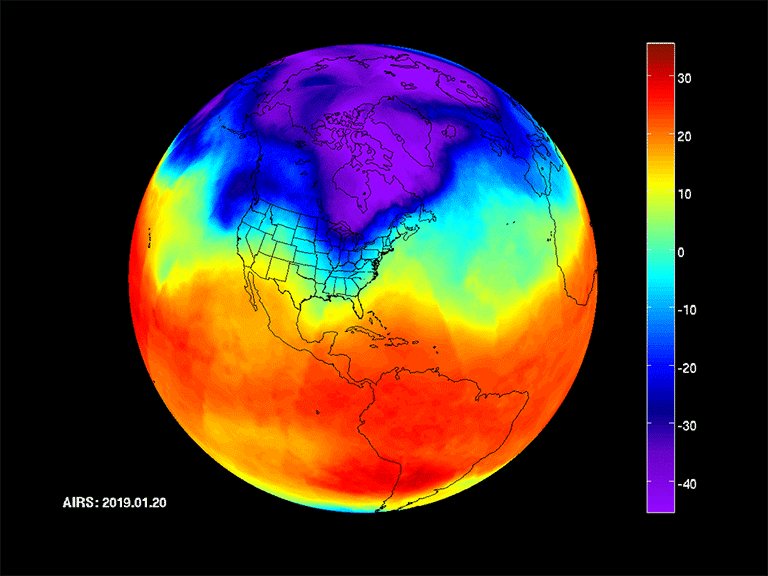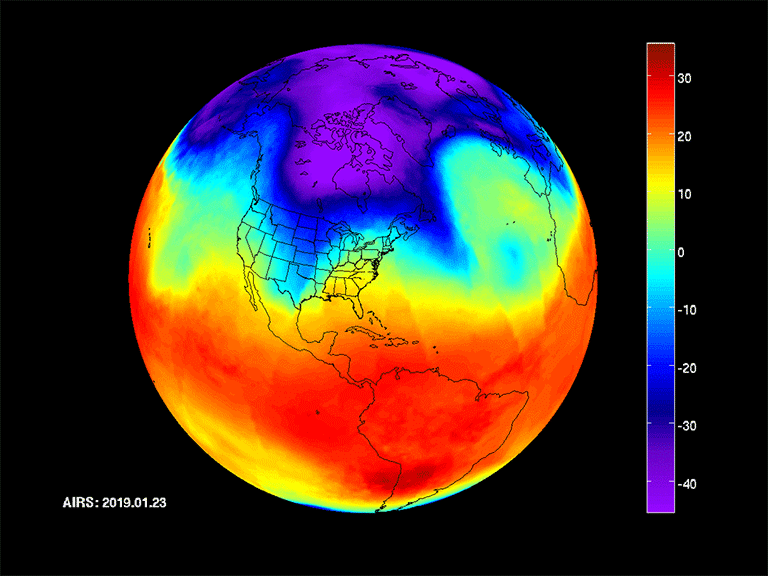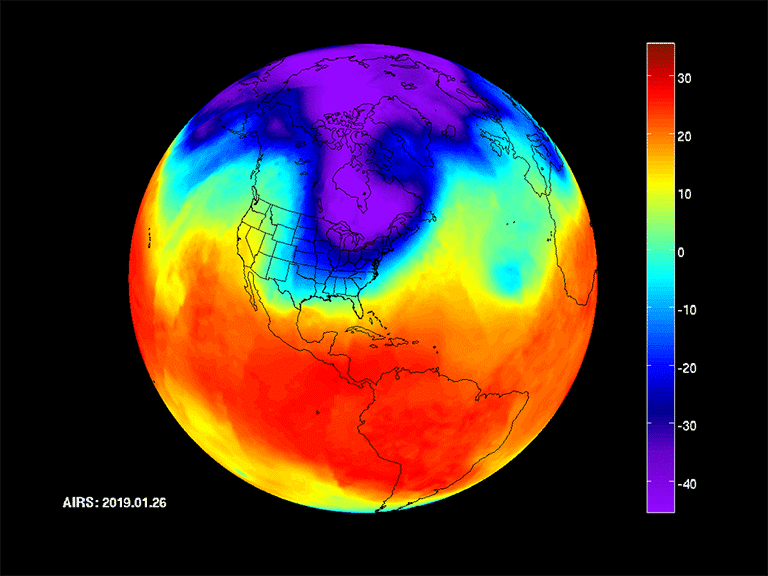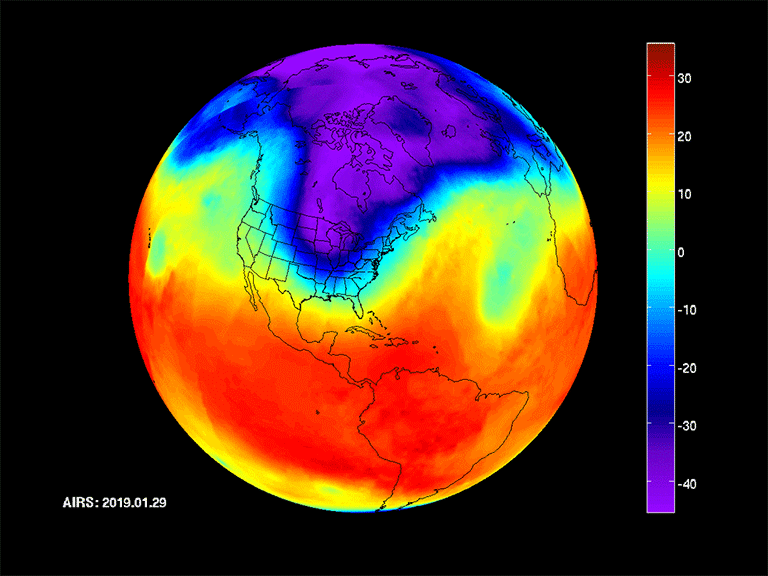
Koppen-Geiger Climate classification of years 1901-2010
Sun and Earth's Climate system
The climate system of the Earth is powered by the Sun.
The energy that the Earth receives from the Sun interacts with the Climate system to produce climate zones.
Earth absorbs energy from the Sun.
When radiation comes in contact with a particle of matter one of three things occurs.
The particle may gain energy by absorbing the radiation.
The particle may transmit the radiation.
The radiation may be reflected off the particle.
What happens to the Sun's light when it reaches the Earth (Out of 100%)
30% is converted into outgoing solar radiation
20% is reflected by clouds.
6% is reflected by the atmosphere.
4% is reflected by the Earth's surface.
70% is outgoing low energy infrared radiation.
Radiated to space from the clouds, atmosphere and indirectly from the Earth-64%.
Radiated directly to space from the Earth-6%.
5 dangerous things that could happen due to global warming.
The Earth's mechanisms get confused
The Eartg is like a living organism, according to the gaia hypothesis. If it's composition is completely changed by a certain virus then a lot of things will change. For example the ice caps are now melting, some places are having floods and some are having droughts.
Worldwide redistribution of growing conditions and fresh water.
If the Earth heats up then animals that have to go outisde and stay there will get very hot and dry. They will also die and some will go extinct. If California gets bad and the crops stop growing then people will start war. Scientists think that Saskatchewan will have California-like conditions by 2100.
Displacement and extinction due to sea level rise.
If the sea level rises too much then many species will die as many places will be submerged. People will have to be evacuated from places like India, China and the phillipenes. scientists think that all this will happen in this century.
Ocean acidification
If carbon dioxide rises then it will also rise in the oceans. This will make the pH of the oceans rise at low rates. While they may seem low, it has been proven that some species need a specific pH to survive. So, a mass extinction occurs when the pH rises.
Stopping of thermohaline circulation
Weather would change or stop completely.
Oceans become a stagnat puddle
Hydrogen sulfide will fill the air.