Disease databases
MalaCards
Phenylketonuria
Description
A rare inborn error of amino acid metabolism characterized by elevated blood phenylalanine and low levels or absence of phenylalanine hydroxylase enzyme. If not detected early or left untreated, the disorder manifests with mild to severe mental disability.
Population frequency
occurs in about 1 in 10,000 births
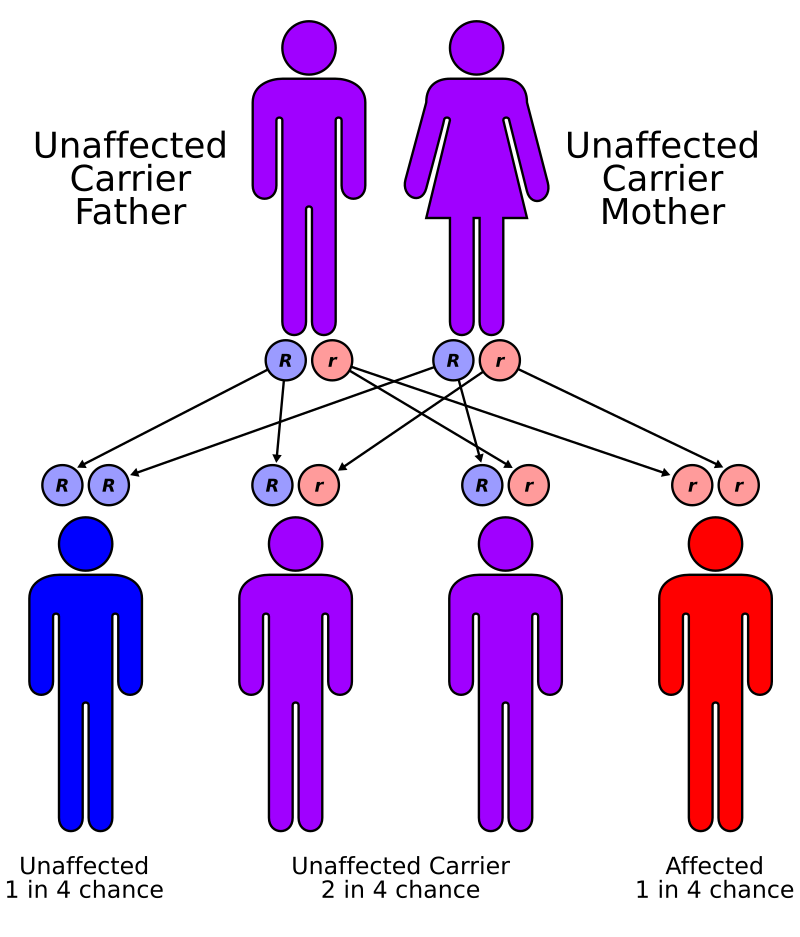
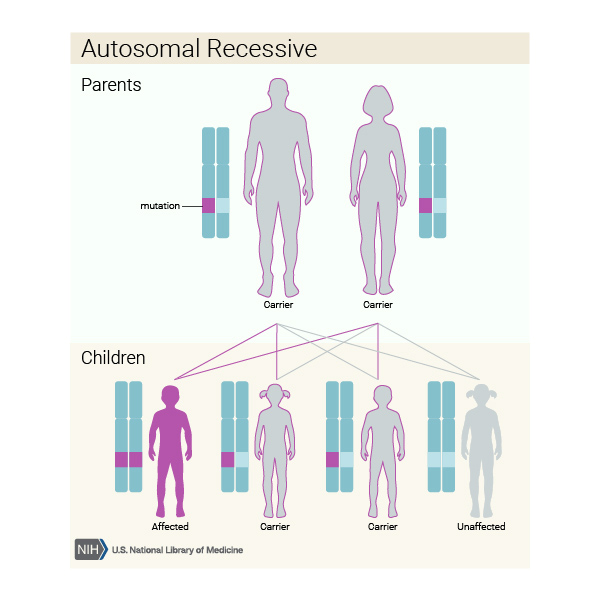
Mode of inheritance
Autosomal recessive
Symptoms
1- aminoaciduria 2- intellectual disability 3- global development delay 4- abnormal facial shape 5- microcephaly
anatomical context
Liver = Liver Lobule = Hepatocytes
drugs and therapeutics
1- Dopamine 2- Tannic acid 3- Benzocaine 4- Melatonin 5- Serotonin
Sickle cell anemia
Description
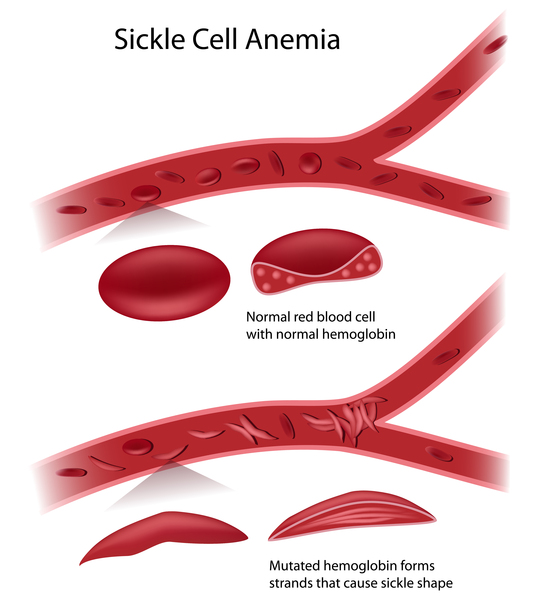
A blood protein disease that is characterized by low number of red blood cells, repeated infections, and periodic episodes of pain, resulting from atypical hemoglobin molecules called hemoglobin S, which can distort red blood cells into a sickle, or crescent, shape.
Population frequency
1-5/10000 (France),1-5/10000 (Germany),1-5/10000 (United States),1-5/10000 (Belgium),1-5/10000 (Europe)
Causes
caused by mutations in the gene that tells our bodies how to make hemoglobin.
Mode in inheritance
autosomal recessive
Synonyms
Sickle cell-hemoglobin c disease syndrome
drugs and therapeutics
1- amodiaquine 2- proguanil 3- fentanyl 4- hydromorphone 5- deferasirox
Symptoms
1- abdominal pain 2- joint and leg pain 3- renal failure 4- increased susceptibility to bacterial infections.
anatomical context
Blood = Peripheral Blood = Erythrocytes
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD)
description
s a genetic disorder that affects red blood cells, which carry oxygen from the lungs to tissues throughout the body.
Population frequency
1 in 10 African American males in the United States.
Causes
mutations in the G6PD gene.
Mode in inheritance
X-linked recessive
drugs and therapeutics
1- piperaquine 2- artenimol 3- clopidorgrel 4- aspirin 5- primaquine
Synonyms
Glucosephosphate Dehydrogenase, G6PD
Disease Ontology
Phenylketonuria
Description
An amino acid metabolic disorder that is characterized by a mutation in the gene for the hepatic enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), rendering it nonfunctional.
Population frequency
affects about 1 in 12000 babies. males and females are affected equally.
Causes
It is due to mutations in the PAH gene, which results in low levels of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase.
Mode of inheritance
autosomal recessive
synonym
1- Folling's disease
2- maternal phenylketonuria
3- phenylalaninemia
4- PKU
Treatment
diet low in phenylalanine
Symptoms
mental retardation, behavioral and movement problems, seizures, and delayed development
Sickle cell anemia
Description
A blood protein disease that is characterized by low number of red blood cells, repeated infections, and periodic episodes of pain, resulting from atypical hemoglobin molecules called hemoglobin S, which can distort red blood cells into a sickle, or crescent, shape.
Population frequency
The disease is estimated to occur in 1 in 500 African Americans and 1 in 1,000 to 1,400 Hispanic Americans.
Causes
Mutations in the HBB gene cause sickle cell disease.
Mode of inheritance
autosomal recessive
synonym
1- drepanocytosis
2- haemoglobin SC disease
3-Hb SC disease
4- Hb-S/Hb-C disease
5- Hb-SS disease without crisis
6- Hemoglobin S disease without crisis
7- hemoglobin SC disease
8- sickle cell anaemia
9- Sickle-cell/Hb-C disease without crisis
Treatment
Vaccination, antibiotics, high fluid intake, folic acid supplementation, pain medication, blood transfusions
Symptoms
Attacks of pain, anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections, stroke
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD)
Description
A carbohydrate metabolic disorder that is characterised by abnormally low levels of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (abbreviated G6PD or G6PDH)
Population frequency
400 million people worldwide. 1 in 10 African American males in the United States.
Causes
results from mutations in the G6PD gene
Mode of inheritance
X-linked recessive

Synonym
1- deficiency of G-6PD
2- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
Treatment
Avoiding triggers, medications for infection, stopping offending medication, blood transfusions
Symptoms
Yellowish skin, dark urine, shortness of breath.
RareDisease
Phenylketonuria
Description
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that is detectable during the first days of life via routine newborn screening. it is a rare metabolic disease tat lead to a severe brain disorders.
Population frequency
ranges from one in 13,500 to 19,000 newborns in the United States.
Causes
(mutations) in the PKU gene
Mode of inheritance
autosomal recessive
Synonyms
1- classical phenylketonuria
2- hyperphenylalanemia
3- phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency
4- phenylalaninemia
5- PKU
Treatment
1- diet low in phenylalanine that required to use amino acid based medical food or formula. 2- severe restriction of dietary natural protein intake. 3- two FDA-approved drugs are also available from the treatment of PKU.
Symptoms
1- weak and feed poorly. 2- vomiting. 3-irritability, and/or a red skin rash with small pimples. 4- severe intellectual disability. 5- psychiatric disorders. 6- seizures.
Sickle cell anemia
Description
It is a genetic disease which red blood cells take the shape of sickle, and that change allowed them to easily be destroyed, causing anemia
Population frequency
1- 0.6 % of the African American population in the United States. 2- one in every 300 – 500 African American newborns.
Causes
Causes by defective hemoglobin A (HbA), a mutation in HBB Gene so B-globin is misshapen
Mode of inheritance
Autosomal recessive
Synonyms
SCD
Treatment
1- for hypoxia, dehydration, and acidosis. They improved with oxygen and fluids.
2- Opiods to manage pain.
3- antibiotics to underlying bacterial infections from acute chest syndrome.
4- blood transfusion
5- for children= penicillin & polysaccharide vaccine
6- bone marrow transplant
7- gene therapy
Symptoms
1- bone pain 2- chest pain 3- severe infections (primarily in children) 4- low levels of circulating red blood cells (anemia). 5- yellowing of the skin (jaundice).
Diagnoses
1- newborn blood spot screen
2- blood smear looking for sickled cells
3- protein electrophoresis
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD)
Description
Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency is a hereditary condition in which red blood cells break down (hemolysis) when the body is exposed to certain foods, drugs, infections or stress. It occurs when a person is missing or has low levels of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Population frequency
About 10%-14% of African-American males are affected.
Causes
caused by an alteration (mutation) in the G6PD gene.
Mode of inheritance
Subtopic
Synonyms
1- G6PD deficiency
2- G6PD
3- Hemolytic anemia due to G6PD deficiency
Treatment
Treatment may involve medicines to treat infection, stopping drugs that are causing red blood cell destruction, and/or transfusions, in some cases.
Symptoms
most G6PD-deficient persons are asymptomatic most of the time; however, any one of them, when exposed to certain triggering factors, can develop acute hemolytic anemia (AHA), which may be life-threatening especially in children.
Diagnoses
If doctors suspect a person is G6PD-deficient, they will conduct a variety of blood tests to confirm a diagnosis and rule out other conditions that cause similar conditions.
OMIM
Phenylketonuria
Description
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an autosomal recessive inborn error of metabolism resulting from a deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase. an enzyme that catalyzes the hydroxylation of phenylalanine to tyrosine, the rate-limiting step in phenylalanine catabolism.
population frequency
PKU occurs in about 1 in 10,000 births
causes
is a result of mutations in the PAH gene.
mode of inheritance
autosomal recessive
synonyms
PHENYLALANINE HYDROXYLASE DEFICIENCY
PAH DEFICIENCY
OLIGOPHRENIA PHENYLPYRUVICA
FOLLING DISEASE
treatments
Phenylketonuria is treatable by a low phenylalanine diet.
symptoms
evere behavioral disturbances, including psychotic disorders, autistic features, hyperactivity, and aggression, as well as self-mutilation
chromosomal location
chromosome 12, q 23.2
diagnosis
Ramus et al. (1992) used PCR amplification of the low levels of mRNA resulting from illegitimate transcription of the PAH gene in fibroblasts and Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphocytes to detect mutations in patients with PKU.
Sickle cell anemia
description
Sickle cell anemia is a multisystem disease associated with episodes of acute illness and progressive organ damage. Hemoglobin polymerization, leading to erythrocyte rigidity and vasoocclusion, is central to the pathophysiology of the disease, but the importance of chronic anemia, hemolysis, and vasculopathy has been established.
population frequency
The estimated number of worldwide annual births of patients with sickle cell anemia is 217,331
causes
Caused by mutation in the hemoglobin beta gene (HBB, 141900.0243)
mode of inheritance
Autosomal recessive
synonyms
- Sickle cell anemia
- Anemia, chronic
- Hemolysis
- Hypoxemia
- Leukocytosis
pathogenesis
HbS has a lower oxygen affinity than normal Hb and polymerizes upon deoxygenation, creating red blood cells that are distorted, resulting in a sickled appearance; adherent, leading to vasoocclusion; and fragile, leading to hemolysis. The clinical consequences of the vascular occlusion are variable, but include bone pain, deep venous thrombosis, acute chest syndrome, and stroke. In an aortic ring bioassay
symptoms
- Increased susceptibility to bacterial infections
- Resistance to falciparum malaria infection - stroke -joint and leg pain
chromosomal location
chromosome 11, p 15.4
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD)
description
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD; EC 1.1.1.49) plays a key role in the production of ribose 5-phosphate and the generation of NADPH in the hexose monophosphate pathway. Because this pathway is the only NADPH-generation process in mature red cells, which lack the citric acid cycle, a genetic deficiency of G6PD (300908) is often associated with adverse physiologic effects
population frequency
Different variants of G6PD are found in high frequency in African, Mediterranean, and Asiatic populations
causes
results from mutations in the G6PD gene.
mode of inheritance
X-Linked
synonyms
G6PD, Hemolytic anemia
symptoms
asymptomatic
chromosomal location
chromosome X, q 28
MedlinePlus
Phenylketonuria
Description
Phenylketonuria (commonly known as PKU) is an inherited disorder that increases the levels of a substance called phenylalanine in the blood.
Population frequency
occurs in 1 in 10,000 to 15,000 newborns in the United States.
Causes
Mutations in the PAH gene
Mode of inheritance
autosomal recessive
Synonyms
1- Deficiency disease, phenylalanine hydroxylase
2- Folling disease
3- Folling's disease
4- PAH deficiency
5- Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency
6- Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency disease
7- PKU
Treatment
Diet of low-protein foods is the best treatment. There are special formulas for newborns. For older children and adults, the diet includes many fruits and vegetables. It also includes some low-protein breads, pastas, and cereals.
Symptoms
1- permanent intellectual disability 2- delayed development 3- behavioral problems 4- psychiatric disorders 5- lighter skin and hair than unaffected family members 6- skin disorders such as eczema
Sickle cell anemia
Description
Sickle cell disease is a group of disorders that affects hemoglobin. People with this disease have atypical hemoglobin molecules called hemoglobin S, which can distort red blood cells into a sickle, or crescent, shape.
Population Frequency
Occur in 1 in 500 African Americans and 1 in 1,000 to 1,400 Hispanic Americans.
Causes
Mutations in the HBB gene cause sickle cell disease.
Mode of inheritance
autosomal recessive
Synonyms
1- HbS disease
2- Hemoglobin S disease
SCD
3- Sickle cell disorders
4- Sickling disorder due to hemoglobin S
Treatments
bone marrow or stem cell transplantation. For the transplant to work, the bone marrow must be a close match. Usually, the best donor is a brother or sister.
Symptoms
1- a low number of red blood cells. 2- repeated infections. 3- periodic episodes of pain. 4- Painful swelling of the hands and feet
5-Fatigue or fussiness from anemia
6- A yellowish color of the skin (jaundice) or the whites of the eyes (icterus)
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD)
Description
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency is a genetic disorder that affects red blood cells, which carry oxygen from the lungs to tissues throughout the body. In affected individuals, a defect in an enzyme called glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase causes red blood cells to break down prematurely. This destruction of red blood cells is called hemolysis.
Population frequency
It affects about 1 in 10 African American males in the United States.
Causes
results from mutations in the G6PD gene.
Mode of inheritance
X-linked
Synonyms
1- Deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate 2- dehydrogenase
3- G6PD deficiency
4- G6PDD
5- Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
Treatments
Treatments include medicines to treat infection, avoiding substances that cause the problem with red blood cells, and sometimes transfusions.
Symptoms
1- paleness (in darker-skinned kids, paleness is sometimes best seen in the mouth, especially on the lips or tongue).
2- extreme tiredness or dizziness
3- fast heartbeat
4- fast breathing or shortness of breath
5- jaundice (the skin and eyes look yellow)
6- an enlarged spleen
7- dark, tea-colored pee