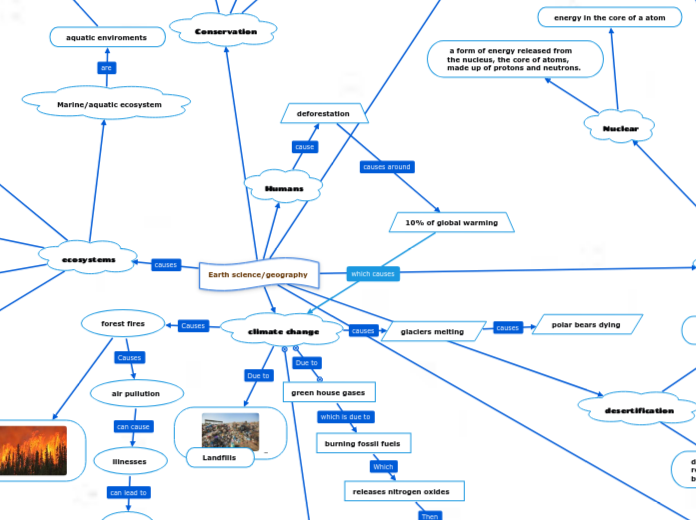
Earth science/geography
Conservation
a careful preservation
and protection of something
caring for these resources
so all living things can benefit
from them now and in the future
protecting our environment
and the wildlife that lives in it
Humans
deforestation
10% of global warming
ecosystems
Marine/aquatic ecosystem
aquatic enviroments
high levles of dissolved salt
limits reproduction
damage aquatic food chain
extincintion of species
forest ecosystem
soil, trees, insects,
animals, birds
a geographic area where plants,
animals, as well as weather and
landscape, work together
grassland ecosystem
large open areas
of grass
area in which the vegetation
is dominated by a nearly
continuous cover of grasses
dessert ecosystem
areas of land characterised
by extremely high or low
temperatures
has a layer of soil that
can be sandy, or stony
tundra ecosystem
cold and dry
receives low amounts
of precipitation
regenerative agriculture
removes carbon from the
atmosphere and puts it back
in the soil
a way of farming that
seeks to actively improve
the health of the environment
Energy sources
Biomass
contains stored chemical energy
from the sun that is produced by plants
through photosynthesis
can be burned directly for heat or
converted to liquid and gaseous
fuels through various processes
Nuclear
energy in the core of a atom
a form of energy released from
the nucleus, the core of atoms,
made up of protons and neutrons.
Solar
The light and heat
that comes from the sun
Coal
non-renewable
energy source
fuel to generate
electric power
Hydropower
power produced
with moving water
one of the oldest power
sources on the planet
Geothermal
heat energy from
the earth
a renewable energy source
because heat is continuously
produced inside the earth
Wind
process by which the wind is
used to generate mechanical
power or electricity
Generating electricity
(wind turbines)
Natural Gas
lower emissions
low cost
desertification
can happen because of
natural or human factors
the process by which
vegetation in drylands
such as grasslands decreases
and eventually disappears
dersetfication can be
reduced
by planting more trees
Landforms
plains
erosional plains
air, ice, or water wears away at
land and little bits of the land are washed away.
Valleys
A long ditch in earths surface
plateaus
a flat, elevated landform that
rises sharply above the
surrounding area on at least one side.
mountain
Mountains are formed by
slow but gigantic movements
of the earth's crust
desserts
a region of land that is very dry
itrevieves low amounts
of perticapation
climate change
glaciers melting
polar bears dying
green house gases
burning fossil fuels
releases nitrogen oxides
everyone is exposed to small bits of nitrogen oxiges
damage the respirtory airways
forest fires
air pullution
illnesses
death
parents cry
Landfiils
Heat
energy that is transferred
from one body to another
as the result of a difference
in temperature
the transfer of thermal
energy between substances
conduction, convection,
and radiation