Functions:
1) Promotes stability of the system
2) Stabilize the aerated system
3) Control the agglomeration of fats globule
4) Modify the texture
5) Increase the shelf-life of the products
6) Improve the texture of fat-based products
Formation of Emulsion:
Requires the dispersion of one phase into small droplets
By homogenization- dispersed phase is broken into small droplets
Factors that effect emulsion stability
1) Droplets size
2) Change in pH or ionic strength
3) Type of emulsifier
4) Viscocity
5) Concentration of emulsifier
Types:

Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsion:
oil droplets are dispersed in continuous water phase.

mayonnaise

milk

cream
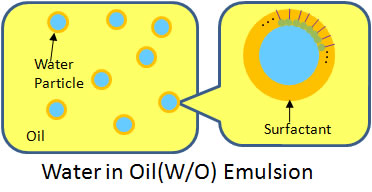
Water-in-Oil (W/O) Emulsion:
water droplets are dispersed in continuous oil phase

margerine

salad dressing
spread