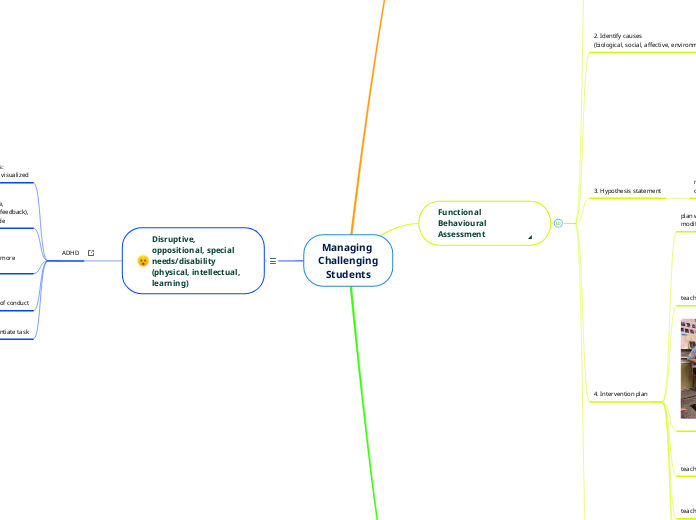
Managing Challenging Students

Change your lens
From "Bad behaviour modification"
to "problem solving" cause of behaviour
behaviour = fever = symptom
problem solve together with child
Challenging = Lacking skills to be successful
(expectations exceed skills)
Functional Behavioural Assessment
(underlying cause)^
1. Define the behaviour concretely
2. Identify causes
(biological, social, affective, environmental)
need multiple sources (maybe contextual, specific teacher)
indirect questioning
to stakeholders
to student themselves
direct observation
ABC analysis
(antecendent, behaviour, consequence)
What's the payoff? (escapes, avoids, gets)
problem solving
flexibility
frustration tolerance
Is there a performance deficit?
(can but not always)
3. Hypothesis statement
manipulate environment,
observe again to confirm
4. Intervention plan
plan ways to avoid trigger,
modify learning enviro
teach student to recognize signs, triggers

feelings cards
more appropriate ways to get attention
teach relaxation skills
animal posture
deep breathing
counting down
teach problem solving skills
plan behavioural contracts, token economy
fade out extrinsic rewards over time
peers, para-professionals (counsellor)
5. Monitor
Interventions
Goal
supports growth
fosters self-esteem
Visualize proper behaviours

Behaviour Learning Ladder
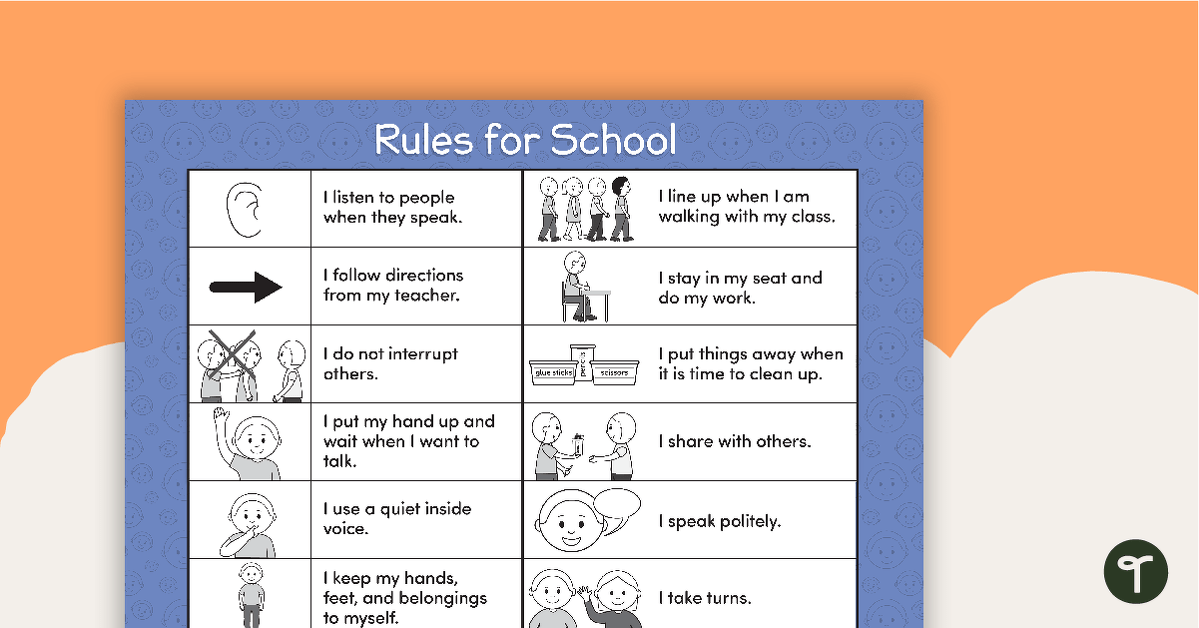
Proper behaviour poster
rewards desirable behaviour
2. Preview (provide predictability)
3. Adjust task difficulty
4. Provide student choice
5. Review model peers
Popular interventions that don't work:
- don't solve problems
- don't teach skills
Disruptive, oppositional, special needs/disability (physical, intellectual, learning)
ADHD
instructions:
clear, brief, visualized
consequences:
more immediate,
more frequent (feedback),
higher magnitude
Reinforcement:
"Positives before negatives"
reinforcers that backup in-class tokens must change more often
Anticipate:
- environment of high energy
- prompt student to recall rules of conduct
Where possible,
modify environment and differentiate task