MedChem Migraine Treatment
Etiology & Pathophys
Vasoactive peptides
-Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)
-Neurokinin A
-Substance P
-Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP)
CGRP & PACAP
-Induce migraine when IV
-cause dilation of cephalic arteries
Serotonin Receptors
-Vascular smooth muscle cells (constriction)
-trigeminal fiber presynaptic boutons (modulate peptide release)
Med Overuse Headache (MOH)
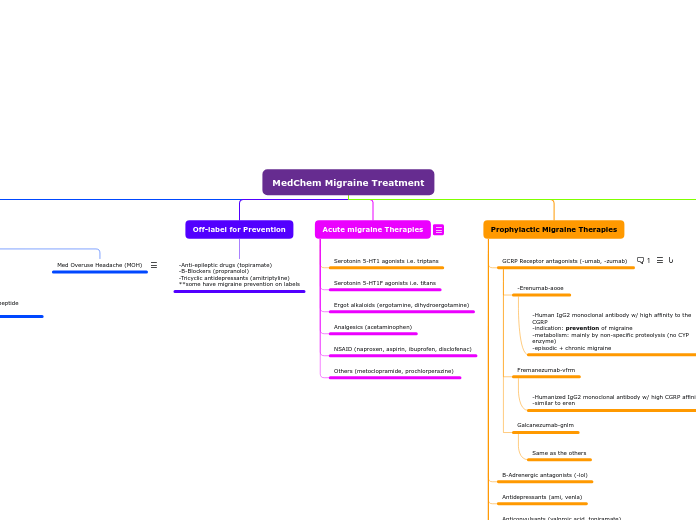
Off-label for Prevention
-Anti-epileptic drugs (topiramate)
-B-Blockers (propranolol)
-Tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline)
**some have migraine prevention on labels
Acute migraine Therapies
Serotonin 5-HT1 agonists i.e. triptans
Serotonin 5-HT1F agonists i.e. titans
Ergot alkaloids (ergotamine, dihydroergotamine)
Analgesics (acetaminophen)
NSAID (naproxen, aspirin, ibuprofen, disclofenac)
Others (metoclopramide, prochlorperazine)
Prophylactic Migraine Therapies
GCRP Receptor antagonists (-umab, -zumab)
-Erenumab-aooe
-Human IgG2 monoclonal antibody w/ high affinity to the CGRP
-indication: prevention of migraine
-metabolism: mainly by non-specific proteolysis (no CYP enzyme)
-episodic + chronic migraine
Fremanezumab-vfrm
-Humanized IgG2 monoclonal antibody w/ high CGRP affinity
-similar to eren
Galcanezumab-gnlm
Same as the others
B-Adrenergic antagonists (-lol)
Antidepressants (ami, venla)
Anticonvulsants (valproic acid, topiramate)
NSAIDs
-block COX2 --> reduce prostaglandins
-PGE2/PGI2 --> reduce threshold to stimulation for nociceptors --> peripheral sensitization
Serotonin 5HT1 agonists (triptans)
Botox
Neurotoxin for chronic migraine. Injection, prevent attacks up to 90 days
-interferes with ACh by breaking a protein req for its release. Stops the activation of pain-receptors
Others (histamine, Mg, MIG-99, riboflavin (B2))
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
TMS is not effective for chronic but for acute it has shown to be effective.
Migraine Treatment
Serotonin 5-HT1 agonists (triptans)
-selective agonists of 5HT1B & 5HT1D receptors
-vasoconstriction (makes it effective in early attack)
-inhibition of vasoactive peptide release from trigeminal neurons (these cause inflammation so it inhibits it)
-inhibition of transmission thru 2nd order neurons
-all triptans have greater efficacies vs. ergot alkaloids
Agents
Suma:
-significant 1st pass effect
-chest discomfort/tightness/pressure/pain
-CI w/ CAD & angina
Serotonin 5-HT1F agonists (ditans)
-inhibit release of CGRP
-inhibit cAMP signaling cascade
-NO constriction
Agents
Lasmiditan
Ergot alkaloids
-broad spectrum of activity on receptors (5HT, alpha, dopamine)
-inhibit trigeminal neurotransmission peripherally + centrally
-vasoconstriction
-similar to triptans
-indole group
Agents: Ergotamine/Dihydroergotamine
-less efficacious vs. triptans
-very low oral bio, +caffeine to improve rate/extent of absorption
-N/V, chest tightness, ergotism
CI:
-Renal/hepatic failure
-coronary, cerebral, peripheral vascular disease
-uncontrolled hypertension
-pregnancy
-nursing mother