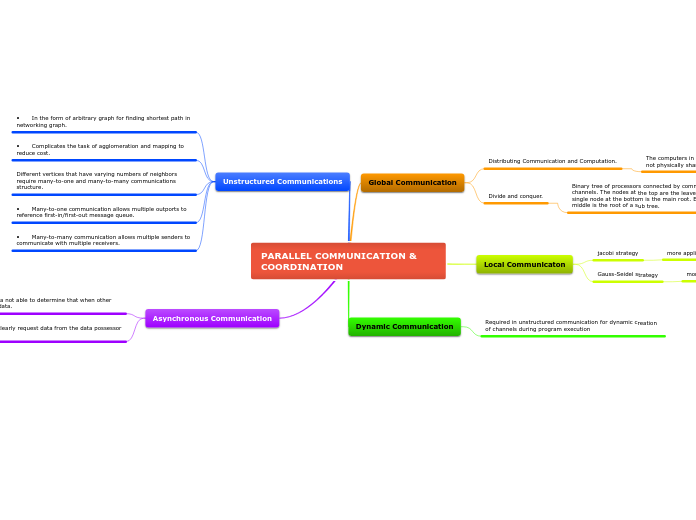
PARALLEL COMMUNICATION & COORDINATION
Global Communication
Distributing Communication and Computation.
The computers in a distributed system are independent and do not physically share memory or processors
Divide and conquer.
Binary tree of processors connected by communication channels. The nodes at the top are the leaves of the tree. The single node at the bottom is the main root. Each node in the middle is the root of a sub tree.
Local Communicaton
jacobi strategy
more applicable to apply on a parallel computer
Gauss-Seidel strategy
more applicable in a sequential program
Dynamic Communication
Required in unstructured communication for dynamic creation of channels during program execution
Unstructured Communications
• In the form of arbitrary graph for finding shortest path in networking graph.
• Complicates the task of agglomeration and mapping to reduce cost.
Different vertices that have varying numbers of neighbors require many-to-one and many-to-many communications structure.
• Many-to-one communication allows multiple outports to reference first-in/first-out message queue.
• Many-to-many communication allows multiple senders to communicate with multiple receivers.
Asynchronous Communication
Is data possess data not able to determine that when other tasks may require data.
consumers must clearly request data from the data possessor
2 solution is