Plant Reproduction
flowering plants
sexual
reproduce from seeds
parts of a flower
reproductive parts
stamen
male
anther
contains one or more pollen sacs that produce pollen grains
filament
a support to the anther

pistil
female
stigma
tip that recieve pollen grains
style
connects the stigma to the ovary
ovary
contains one or more ovules;develops into a fruit which protects the seeds inside
ovule
contains the egg nuceus;undevelop seed with a tiny egg inside
non-reproductive parts
petals
sepals
pollination
Pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma by wind or by animals
cross-pollination
self-pollination
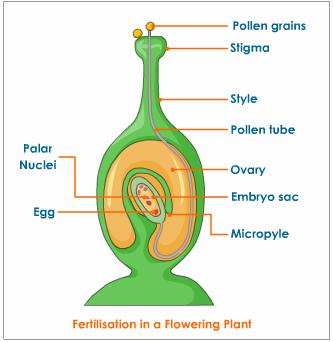
fertilization
Fertilisation occurs when the pollen grain enters the ovary and fuses with an ovule to form a fertilised egg.Upon fertilization,the ovules inside the ovary develop into seeds and the ovary develops into a fruit.
seed dispersal
Seed dispersal is the scattering of seeds or fruits.It increases the chances of survival.
wind
seeds that can fly or glide
stiff wings
E.G.lime and sycamore seeds
Lime seeds
thin wings
E.G.alsomitra and Tecoma seeds

Tecoma seeds
feathery tails
Pulsatilla seeds

Pulsitilla
Subtopic
seeds that drift in the wind
daisy seeds have a flat disk of fine hair to produce a parachute
fruits have wing-like structures
E.G.angsana and shorea fruits

Shorea fruits
seeds that are released from their pods by the wind
poppy and evening primrose seeds need the wind to bend thier stalks to allow the seeds to fall out from thier pods

Evening primrose seeds
water
seeds are light and can float, some may have fluff that enhances buoyancy
E.G.willow and foxglove seeds

Foxglove seeds
Fruits and seeds that have woody, waterproof coverings that help them float
E.G.coconut and pong pong fruit

Coconut fruits
animals
seeds with attractive, fleshy and juicy fruits scattered by humans animals
durians and mangoes have big, hard and inedible seeds that will be thrown away after the flesh is eaten

Mangoes
guavas and raspberrieshave small,hard seeds that are swallowed and passed out in droppings

Guavas
seeds with clinging hooks or spines that stick onto the fur or feathers of animals and clothes or bags of humans
mimosa and lovegrass seeds

Mimosa seeds
splitting
fruits split open with explosive action
E.G.rubber and balsam fruits

Rubber fruits
fruits split open, but without an explosive action
E.G.african tulip and kapok fruits

African tulip
gravity
large,round and heavy fruits drop straight off the tree onto the ground when they are ripe
durian fruits

Durian
germination
Germination is a process whereby seeds grow into new plants under favourable conditions.

From seed to seedling is called germination
conditions for germination
air
water
warmth
asexual
reproduce by vegetative propagation
natural
leaf
E.G.begonia
sucker
E.G.banana
underground stem
bulb
E.G.onion
corm
E.G.water chestnut
Rhizome
E.G.ginger
tuber
E.G.potato
runner
E.G.strawberry

Strawberry
non-flowering plant
reproduce from spores
E.G.fern

fern
