PROKARYOTES (EXTERNAL)
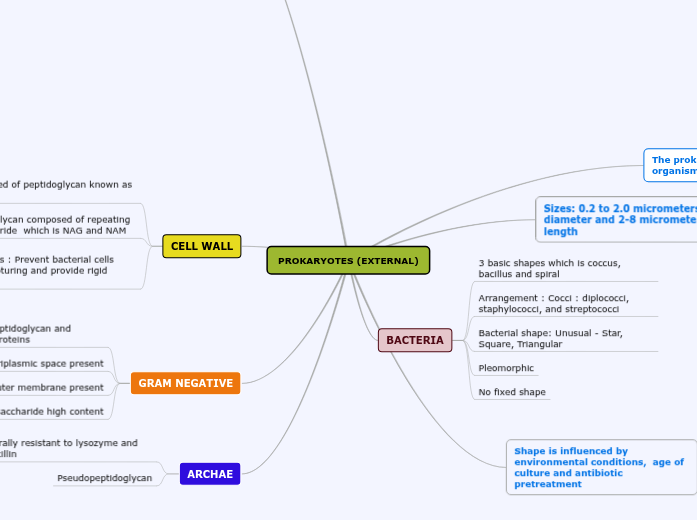
The prokaryotes are group of organisms that lack a cell nucleus
Sizes: 0.2 to 2.0 micrometers in diameter and 2-8 micrometer in length
BACTERIA
3 basic shapes which is coccus, bacillus and spiral
Arrangement : Cocci : diplococci, staphylococci, and streptococci
Bacterial shape: Unusual - Star, Square, Triangular
Pleomorphic
No fixed shape
Shape is influenced by environmental conditions, age of culture and antibiotic pretreatment
Structures external to the cell wall
Glycocalyx
Flagella
Axial Filaments
Fimbriae and Pili
Can occur are the poles of the bacterial cell and evenly distributed
Transfer of DNA from one cell to another and called as sex pili
Bundles of fibrils that arise at the ends of the cell beneath the outer sheath
Motility and attachment to surface
Monotrichous- one flagellum
Amphitrichous-one flagellum at each end of the cell
Peritrichous - Spread over entire surface of cell
Lophotrichous - cluster of flagella at one or both ends
Made of sugars called extracellular polysaccharide
If substance is organized and firmly attached to the cell wall is capsule
Of substance is unorganized and one loosely attached to the cell wall, it's a slime layer
Protection from phagocytosis
Source of nutrients
CELL WALL
Composed of peptidoglycan known as murein
Peptidoglycan composed of repeating dissacharide which is NAG and NAM
Functions : Prevent bacterial cells from rupturing and provide rigid platform
Gram Positive
Thick peptidoglycan and smaller than the Gram Negative
Exoenzymes are secreted
Teichoic acid present
GRAM NEGATIVE
Thin layer of peptidoglycan and bonded to lipoproteins
Periplasmic space present
Outer membrane present
Lipopolysaccharide high content
ARCHAE
Naturally resistant to lysozyme and penicillin
Pseudopeptidoglycan