Psych Final Terms
Motivation
Mindset
- how you view yourself
- fixed abilities: pessimistic, learned helplessness
- changeable abilities: you don't understand it yet
you "set" yourself up to succeed or fail
Self Actualization

Intrinsic motivation

Your interests based on internal rewards, motivates someones behavior to increase because it is rewarding intrinsically
inter- within
BioPsychology
Dopamine
-"feel good" neurotransmitter; control of movement and sensations of pleasure
- increase levels: Schizophrenia
- decrease levels: Parkinson's
Corpus Callosum

Toni Cotignola, Alanna Schwarz, Sarah Katz, Matt Maffa
Developmental Psychology
Personal Fable
there has never been anyone like me, egocentrism
Interaction with parents about how they haven’t been like you (son). “Dad I’m not you”

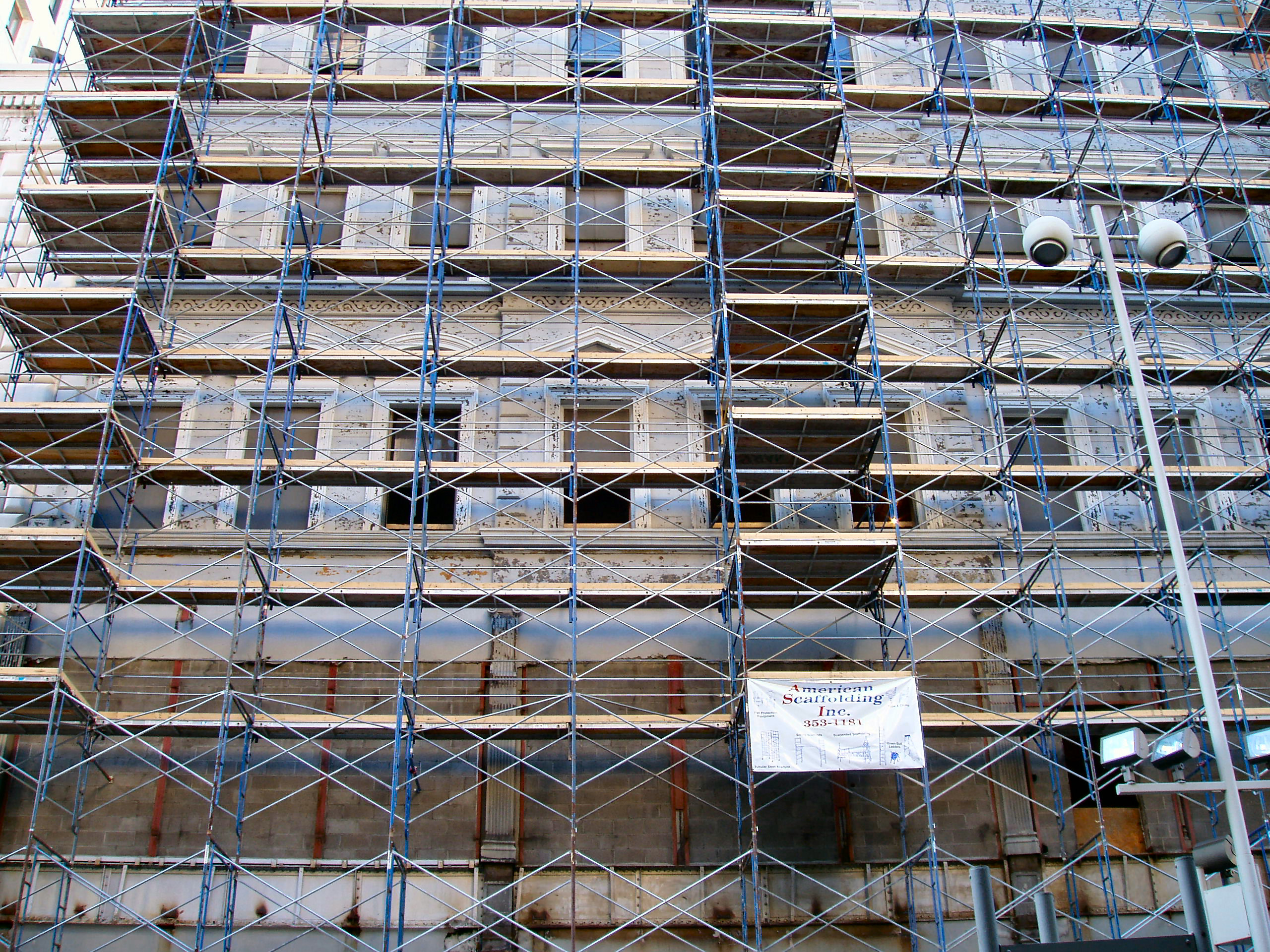
Scaffolding
teachers help students move to new levels of understanding with just a little bit of help; climb the "academic ladder"
scaffolding on a building- climb the building

Imaginary Audience

Object Permanence
achieved in the preoperational stage, playing peek-a-boo with a child. Seeing something, then it’s covered and you know its still there is when it’s achieved
"Perm" - supposed to be permanent curls but it’s not if you wash it out.

Conventional Moral Thinking
- focus is on what others, including your family, might think or what society’s law says about the matter
- double edged sword
"Convent" - cult, and other’s takes on it
Post-Conventional Moral Thinking

pst
Displacement
Displacement
when your angry about something and you yell at someone else that is not involved.

Doing poorly on a test and then getting mad at your friend later for something trivial. Meant, didn’t mean it when you yelled at them
Main topic
Social Psychology
Deindividuation
lessening of personal identity & responsibility; anonymity of crowd (riot)

Protester's mother pulls son from crowd
Diffusion of Responsibility

Fundamental Attribution Theory

Confirmation Bias
tendency to take information and interpret it in your favor
"firm" - firm in your own beliefs
gun control: only reading articles that support your beliefs

Cognitive Dissonance
when someone says one thing but they mean another, someone’s actions don’t reflect their personality
"Diss" - you feel dissed when they do something hypocritical
Social Loafing
When a person doesn't do their share of the work, causing a strong need for assigned roles.

Reciprocity
-responding to a positive action with another positive action
- you do something for me & I feel like I should do something for you
"city" - many people holding doors for each other
Social Identity

Stereotype Vulnerability

Learned Helplessness

foot in the door

Subtopic
Learning/Memory
Classical Conditioning
learning process that occurs when two stimuli (unconditioned stimulus and unconditioned response) are paired together repeatedly
Pavlov’s Dogs

Token Economy

Operant Conditioning
training through conditioning
Negative Reinforcement

Taking away something to punish a behavior, or taking an action in order to stop a "punishment"
Variable Reinforcement

Main topic
REDI
Retrieval Practice
trying to see what you actually remember when studying without looking at your notes
Trial, not having notes to go off of and having to know the situation
Distributed Practice