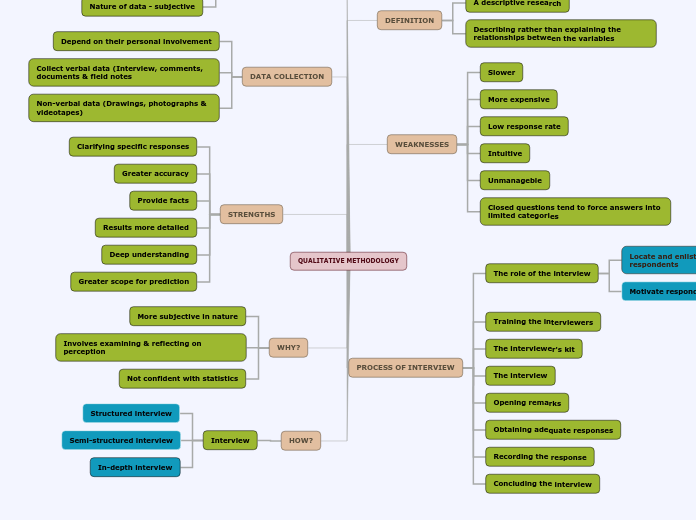
QUALITATIVE METHODOLOGY
DEFINITION
A descriptive research
Describing rather than explaining the relationships between the variables
WEAKNESSES
Slower
More expensive
Low response rate
Intuitive
Unmanageble
Closed questions tend to force answers into limited categories
PROCESS OF INTERVIEW
The role of the interview
Locate and enlist cooperation of respondents
Motivate respondents to do a good job
Training the interviewers
The interviewer's kit
The interview
Opening remarks
Obtaining adequate responses
Recording the response
Concluding the interview
DATA ANALYSIS
Inductive reasoning
To make specific observation, draw inferences about larger phenomenon
Nature of data - subjective
DATA COLLECTION
Depend on their personal involvement
Collect verbal data (Interview, comments, documents & field notes
Non-verbal data (Drawings, photographs & videotapes)
STRENGTHS
Clarifying specific responses
Greater accuracy
Provide facts
Results more detailed
Deep understanding
Greater scope for prediction
WHY?
More subjective in nature
Involves examining & reflecting on perception
Not confident with statistics
HOW?
Interview
Structured interview
Semi-structured interview
In-depth interview