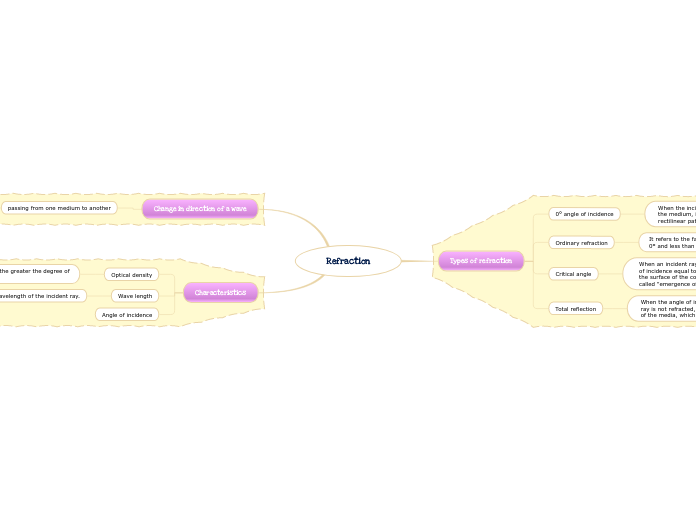
Refraction
Types of refraction
0° angle of incidence
When the incident ray arrives perpendicular to the surface of the medium, it is not refracted but continues with the rectilinear path it had.
This is a theoretical assumption that does not occur in reality.
Ordinary refraction
It refers to the fact that the angle of incidence is greater than 0º and less than 90º.
Critical angle
When an incident ray crosses another medium with an angle of incidence equal to 90º, when it emerges it does so along the surface of the considered medium, producing what is called "emergence of friction".
Total reflection
When the angle of incidence is greater than 90º, the incident ray is not refracted, but is reflected on the separation surface of the media, which acts as a mirror.
Change in direction of a wave
passing from one medium to another
Caused by its change in speed
Characteristics
Optical density
The greater the difference in density, the greater the degree of displacement.
Wave length
The wavelength of the incident ray.
Angle of incidence