Statistics ch1
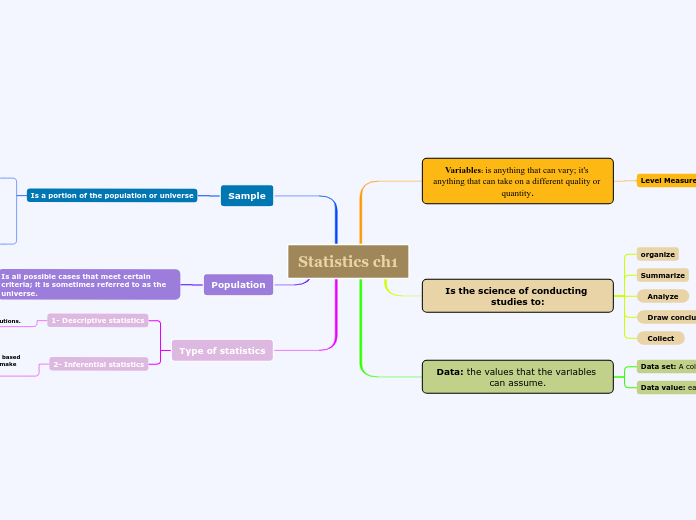
Variables: is anything that can vary; it's anything that can take on a different quality or quantity.
Level Measurement of the data:
Nominal level
Is based upon categories that are mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive.
Ordinal level
Has all the characteristics of nominal level of measurement, plus the notion of order (i.e., greater than and less than).
Interval level
Has all the characteristics of the ordinal level of measurement, plus an underlying scale of equal intervals.
Ratio level
Has all the characteristics of the interval level of measurement, plus what is typically referred to as legitimate zero point.
Is the science of conducting studies to:
organize
Summarize
Analyze
Draw conclusion from data
Collect
Data: the values that the variables can assume.
Data set: A collection of data values
Data value: each value in the data set.
Sample
Is a portion of the population or universe
the four methods of sampling are
1- random sampling
2- systematic sampling
3- stratified sampling
4- cluster sampling
Error
Sampling error
Nonsampling error
Population
Is all possible cases that meet certain criteria; it is sometimes referred to as the universe.
Type of statistics
1- Descriptive statistics
Are used to describe or summarize data distributions.
Average median standard deviation mode
2- Inferential statistics
Are used to make statements about a population, based upon information from a sample; they're used to make inferences.
Use probability: the chance of an event occurring
the area of it called hypothesis testing: a decision making process for evaluating claims about a population, based on inform. obtained from samples.