Tips for Developing Academic Reading Skills

Pre-viewing (before you read)

Brainstorming
List the information about title.

Pre-questions
Questions you expect to be answered.

Visual Aids
Search for pictures related to your tittle.

Overviews
Discuse information about the assignment.

Vocabulary previews
Learn unfamiliar keywords

Author consideration
Point of view
Reason for writing

Purpose for reading
Focus your attention

KWL
What do I know?
What do I want to learn?
What did I learn?

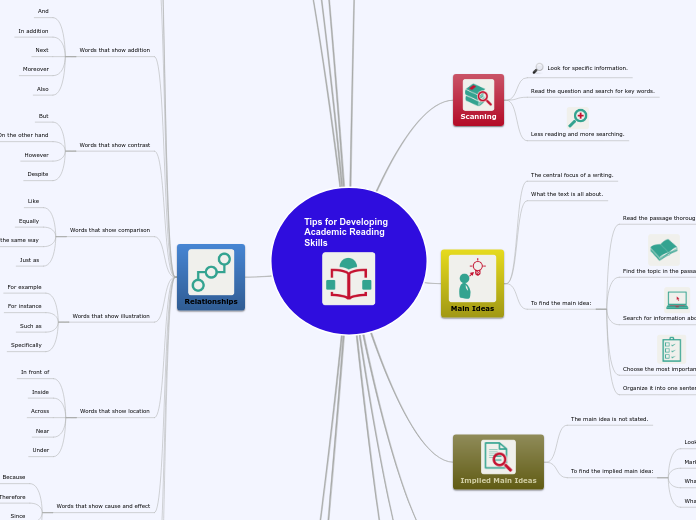
Scanning
Look for specific information.
Read the question and search for key words.

Less reading and more searching.

Main Ideas
The central focus of a writing.
What the text is all about.
To find the main idea:
Read the passage thoroughly.

Find the topic in the passage.

Search for information about the topic.

Choose the most important details.
Organize it into one sentence.

Implied Main Ideas
The main idea is not stated.
To find the implied main idea:
Look for repeated words.
Mark major supporting details.
What is the topic of those details?
What point is being made about the topic?

Inferences
Ideas that are not stated directly.
To make inferences in reading:
Never lose sight of the available information.
Use your background information.
Consider the alternatives.

Argumentation
A rational discussion.
Support a point of view about some matter.
Evidence to supporting a point of view.
Cite sources
Cite examples
Reasons plausible

Active reading and study
Ask yourself
What is the point?
What is the support for the point?
Strategies
Questioning
Connecting
Predicting
Reviewing
Evaluating
Visualizing
Skimming

Identify the main idea.
To do skimming you should
Read the title, subtitles and subheadings.

Look at the ilustrations.
Read the first and last sentence of each sentence.
Look for keywords
Look for topic sentence

Semantic Mapping
Visual strategy
Vocabulary expasion

Extension of knowledge
It includes the concept word.
It includes categories and examples.

Supporting Details
Facts
Reasons
Examples
Explain a main idea.
They are marked by addition words.

Relationships
It makes the ideas clear.
Transitions
It shows the connections between ideas.
Words that show time
First
Next
Then
Often
After
Now
Words that show addition
And
In addition
Next
Moreover
Also
Words that show contrast
But
On the other hand
However
Despite
Words that show comparison
Like
Equally
In the same way
Just as
Words that show illustration
For example
For instance
Such as
Specifically
Words that show location
In front of
Inside
Across
Near
Under
Words that show cause and effect
Because
Therefore
Since
As a result
Words that summarize or conclude
In summary
In conclusion
In brief
In other words
Words that clarify
Of course
In fact
To be sure
Evidently

Purpose and Tone
Tone
The author's attitude toward the topic.
Objective tone
Facts
Reasonable explanations
Subjective tone
Feelings
Opinions
Purpose
The author's reason for writing.
It will drive the main idea:
To inform
To entertain
To persuade

Critical Reading
A fact
It can be proved true.
An opinion
A belief
A judgment
It can not be proved true.
To read critically you need:
Separating fact from opinion
Detecting propaganda
Recognizing erors in reasoning