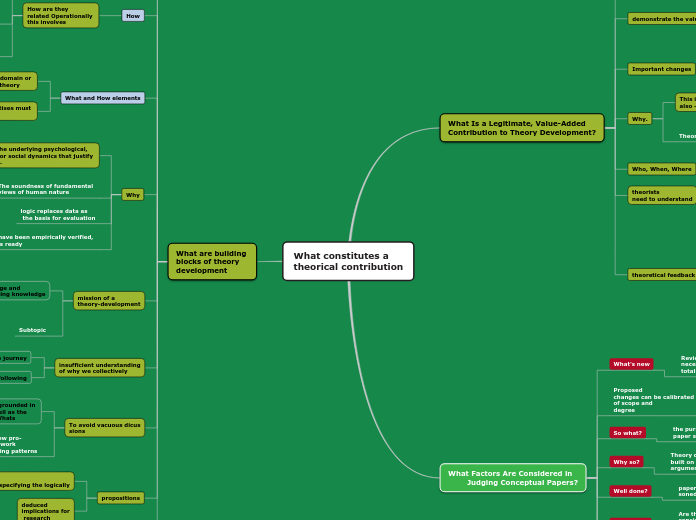
What constitutes a
theorical contribution
What Is a Legitimate, Value-Added
Contribution to Theory Development?
What and How
Although, in principle, it is
possible to make an important theoretical
contribution
adding or subtracting factors
(Whats)
demonstrate the value
pro
posed change
Identify how
this change affects the accepted relationships
between the variables (Hows
)
Important changes
in a theory's What and
How ire frequently stimulated
Why.
This is probably the most fruitful, but
also -he most difficult
involves borrowing a per-
spective from other fields
Theories
are challenged
because their as-
sumptions have been proven
unrealistic
Who, When, Where
insuficient to point out limitations
in current conceptions
theorists
need to understand
why this anomaly exists, so
that they can revise the How and What
theoretical feedback loop.
First
proposed improvements addressing
only a
single element
Second
theoretical critiques
should marshal
compelling evidence
empirical
its predictions are inconsistent with
the data accumulated from several studies
epistemological
its assumptions are invalid
given information from
another field
Third
In general, theoretical critiques should
propose remedies or alternatives
What Factors Are Considered in
Judging Conceptual Papers?
What's new
Reviewers are not
necessarily looking for
totally new theories
Proposed
changes can be calibrated in terms
of scope and
degree
So what?
the purpose of the standard theoretical
paper should be to alter research practice
Why so?
Theory development papers should be
built on a foundation of convincing
argumentation
Well done?
paper reflect sea-
soned thinking
Done well?
Are the paper's format and content
consistent
with the specifications
in the Notice
Why now?
interviewers give low marks to
papers they perceive are
redundant, unconnected, or antiquated
Who cares?
A paper may
be technically adequate but inherently uninter-
estinc to most of our broad audience
What are building
blocks of theory
development
theory development
a complete theory must con-
tain four essential elements
What
variables
constructs
Two criteria
the "right" factors:
comprehensiveness
parsimony
concepts
delete unnecessary or invalid
elements than it is to justify additions.
How
How are they
related Operationally
this involves
using
"arrows"' to
connect the "boxes
it typically in-
troduces causality.
the researcher
may be unable to adequately
test these links
What and How elements
constitute toe domain or
subject of the theory
Not all theoretical treatises must
contain figures
A visual representation
often clarifies the author's
Why
What are the underlying psychological,
economic, or social dynamics that justify
the factors.
the theory's
assumptions
the theoretical glue
that welds
the model together.
The soundness of fundamental
views of human nature
provide the basis for judging the reason
ableness of the proposed conceptualization
logic replaces data as
the basis for evaluation
If all links have been empirically verified,
the model is ready
mission of a
theory-development
is to challenge and
extend existing knowledge
Why research
Is conducted has important im-
plications for the link between theory develop-
ment and empirical research
Subtopic
insufficient understanding
of why we collectively
Started an investigative journey
What theoretical direction we are following
To avoid vacuous dicus
sions
should be well grounded in
the Whys, as well as the
Hows and the Whats
What and How pro-
vide a framework
for interpreting patterns
propositions
they should
be limited to specifying the logically
deduced
implications for
research
Who, Where, When
conditions place
limitations on the propositions
generated from a
theoretical model.
These temporal and contex-
tual factors set the boundaries of
generalizability
Sensitivity to context is especially
important
for theories based on experience.
discovered through sub-
sequent tests of the initial, rudimentary
theoretical statement