av Carlos Carlos för 1 år sedan
121
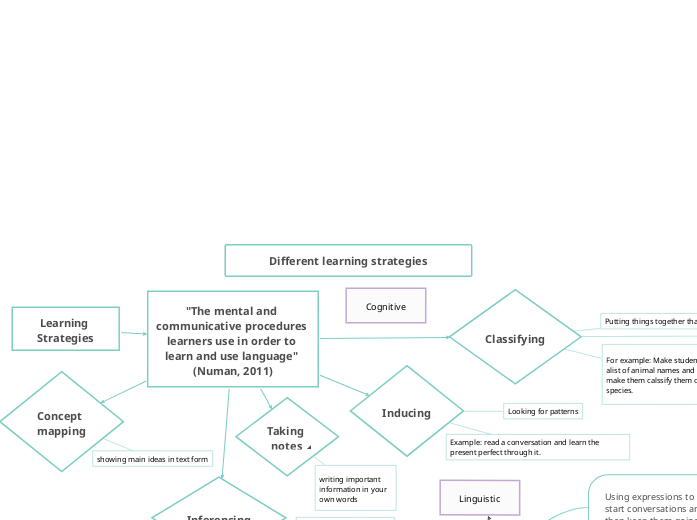
Different learning strategies
av Carlos Carlos för 1 år sedan
121

Mer av detta
Examples: Read the title in a book chapter and prdict what the contents will be.
Predicting what is to come in the learning process