av Edward King för 6 årar sedan
233
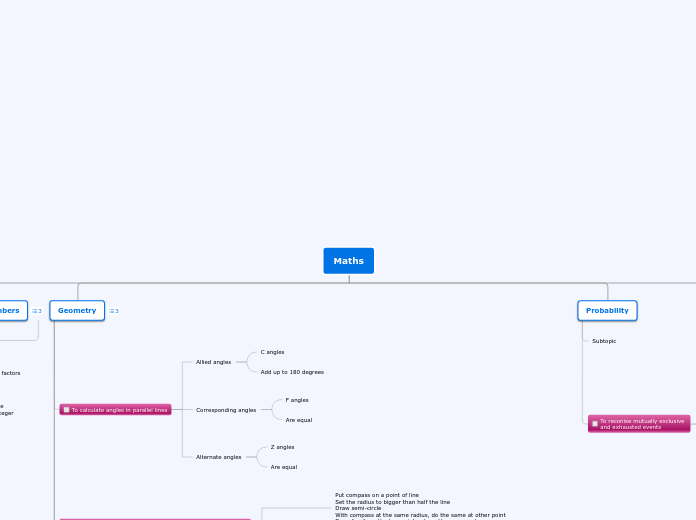
Maths
The provided text covers several important mathematical concepts and operations. It begins with the fundamentals of working with numbers, specifically focusing on performing multiplications and divisions involving negative numbers.